Minimally invasive ureteroplasty with lingual mucosal graft for complex ureteral stricture: analysis of surgical and patient-reported outcomes
- PMID: 38166222
- PMCID: PMC10947641
- DOI: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2023.0393
Minimally invasive ureteroplasty with lingual mucosal graft for complex ureteral stricture: analysis of surgical and patient-reported outcomes
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate objective treatment efficacy and safety, and subjective patient-reported outcomes in patients with complex ureteral strictures (US) undergoing minimally invasive lingual mucosal graft ureteroplasty (LMGU).
Materials and methods: We prospectively enrolled patients underwent robotic or laparoscopic LMGU between May 2020 and July 2022. Clinical success was defined as symptom-free and no radiographic evidence of re-obstruction. Patient-reported outcomes, including health-related quality of life (HRQoL), mental health status and oral health-related quality of life (OHRQoL), were longitudinally evaluated before surgery, 6 and 12 months postoperatively.
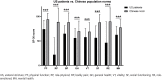
Results: Overall, 41 consecutive patients were included. All procedures were performed successfully with 32 patients in robotic approach and 9 in laparoscopic. Forty (97.56%) patients achieved clinical success during the median follow-up of 29 (range 15-41) months. Although patients with complex US experienced poor baseline HRQoL, there was a remarkable improvement following LMGU. Specifically, the 6-month and 12-month postoperative scores were significantly improved compared to the baseline (p < 0.05) in most domains. Twenty-eight (68.3%) and 31 (75.6%) patients had anxiety and depression symptoms before surgery, respectively. However, no significant decrease in the incidence of these symptoms was observed postoperatively. Moreover, there was no significant deterioration of OHRQoL at 6 months and 12 months postoperatively when compared to the baseline.
Conclusions: LMGU is a safe and efficient procedure for complex ureteral reconstruction that significantly improves patient-reported HRQoL without compromising OHRQoL. Assessing patients' quality of life enables us to monitor postoperative recovery and progress, which should be considered as one of the criteria for surgical success.
Keywords: Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedures; Plastic Surgery Procedures; Quality of Life.
Copyright® by the International Brazilian Journal of Urology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures



References
-
- Li B, Xu Y, Hai B, Liu B, Xiang Y, Hua X, et al. Laparoscopic onlay lingual mucosal graft ureteroplasty for proximal ureteral stricture: initial experience and 9-month follow-up. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016;48:1275–1279. - PubMed
-
- You Y, Gao X, Chai S, Chen J, Wang J, Zhang H, et al. Oral mucosal graft ureteroplasty versus ileal ureteric replacement: a meta-analysis. BJU Int. 2023;132:122–131. - PubMed
-
- Yang K, Fan S, Wang J, Yin L, Li Z, Xiong S, et al. Robotic-assisted Lingual Mucosal Graft Ureteroplasty for the Repair of Complex Ureteral Strictures: Technique Description and the Medium-term Outcome. Eur Urol. 2022;81:533–540. - PubMed
-
- Liang C, Wang J, Hai B, Xu Y, Zeng J, Chai S, et al. Lingual Mucosal Graft Ureteroplasty for Long Proximal Ureteral Stricture: 6 Years of Experience with 41 Cases. Eur Urol. 2022;82:193–200. - PubMed
-
- Rui Wang, Cheng Wu, Ma XQ, Zhao YF, Yan XY, Jia He. Health-related quality of life in Chinese people: a population-based survey of five cities in China. Scand J Public Health. 2011;39:410–418. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
