Link between m6A modification and infiltration characterization of tumor microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 38166412
- PMCID: PMC10903232
- DOI: 10.1177/15353702231214266
Link between m6A modification and infiltration characterization of tumor microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
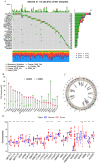
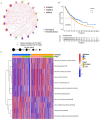
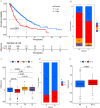
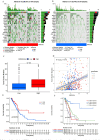
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA methylation plays a pivotal role in immune responses and the onset and advancement of cancer. Nonetheless, the precise impact of m6A modification in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and its associated tumor microenvironment (TME) remains to be fully elucidated. Here, we distinguished distinct m6A modification patterns within two separate LUAD cohorts using a set of 21 m6A regulators. The TME characteristics associated with these two patterns align with the immune-inflamed and immune-excluded phenotypes, respectively. We identified 2064 m6A-related genes, which were used as a basis to divide all LUAD samples into three distinct m6A gene clusters. We applied a scoring system to evaluate the m6A gene signature of the m6A modification pattern in individual patients. To authenticate the categorization significance of m6A modification patterns, we established a correlation between m6A score and TME infiltration profiling, tumor somatic mutations, and responses to immunotherapy. A high level of m6A modification may be associated with the aggressiveness and poor prognosis of LUAD. Further studies should investigate the mechanism of action of m6A regulators and m6A-related genes to improve the diagnosis and treatment of patients with LUAD.
Keywords: immunotherapy; lung adenocarcinoma; m6A; stroma; tumor microenvironment; tumor somatic mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Correlation analysis of m6A-modified regulators with immune microenvironment infiltrating cells in lung adenocarcinoma.PLoS One. 2022 Feb 23;17(2):e0264384. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264384. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35196365 Free PMC article.
-
The significance of m6A RNA methylation modification in prognosis and tumor microenvironment immune infiltration of cervical cancer.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Jul 1;101(26):e29818. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029818. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35777046 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) regulator expression pattern correlates with the immune landscape in lung adenocarcinoma.Gene. 2022 Aug 20;836:146639. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146639. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Gene. 2022. PMID: 35700805
-
[Comprehensive Analysis of the Relationship between m6A Methylation Patterns and Immune Microenvironment in Lung Adenocarcinoma].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022 May 20;25(5):311-322. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2022.103.02. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35599007 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Molecular characterization, biological function, tumor microenvironment association and clinical significance of m6A regulators in lung adenocarcinoma.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Jul 20;22(4):bbaa225. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa225. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33003204
Cited by
-
IGF2BP2 promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression by regulating LOX1 and tumor-associated neutrophils.Immunol Res. 2024 Dec 17;73(1):16. doi: 10.1007/s12026-024-09563-9. Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 39688738
References
-
- Sun T, Wu R, Ming L. The role of m6A RNA methylation in cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 2019;112:108613. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

