Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the ADH gene family under diverse stresses in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.)
- PMID: 38166535
- PMCID: PMC10759372
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-023-09813-4
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the ADH gene family under diverse stresses in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.)
Abstract
Background: Alcohol dehydrogenases (ADHs) are the crucial enzymes that can convert ethanol into acetaldehyde. In tobacco, members of ADH gene family are involved in various stresses tolerance reactions, lipid metabolism and pathways related to plant development. It will be of great application significance to analyze the ADH gene family and expression profile under various stresses in tobacco.
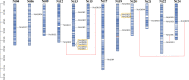
Results: A total of 53 ADH genes were identified in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) genome and were grouped into 6 subfamilies based on phylogenetic analysis. Gene structure (exon/intron) and protein motifs were highly conserved among the NtADH genes, especially the members within the same subfamily. A total of 5 gene pairs of tandem duplication, and 3 gene pairs of segmental duplication were identified based on the analysis of gene duplication events. Cis-regulatory elements of the NtADH promoters participated in cell development, plant hormones, environmental stress, and light responsiveness. The analysis of expression profile showed that NtADH genes were widely expressed in topping stress and leaf senescence. However, the expression patterns of different members appeared to be diverse. The qRT-PCR analysis of 13 NtADH genes displayed their differential expression pattern in response to the bacterial pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum L.
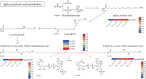
Infection: Metabolomics analysis revealed that NtADH genes were primarily associated with carbohydrate metabolism, and moreover, four NtADH genes (NtADH20/24/48/51) were notably involved in the pathway of alpha-linolenic acid metabolism which related to the up-regulation of 9-hydroxy-12-oxo-10(E), 15(Z)-octadecadienoic acid and 9-hydroxy-12-oxo-15(Z)-octadecenoic acid.
Conclusion: The genome-wide identification, evolutionary analysis, expression profiling, and exploration of related metabolites and metabolic pathways associated with NtADH genes have yielded valuable insights into the roles of these genes in response to various stresses. Our results could provide a basis for functional analysis of NtADH gene family under stressful conditions.
Keywords: Alcohol dehydrogenases (ADH); Gene expression; Nicotiana tobacum L.; Phylogenetic analysis; Stress.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Functional and evolutionary comparative analysis of the DIR gene family in Nicotiana tabacum L. and Solanum tuberosum L.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jul 5;25(1):671. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10577-8. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38970011 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the R2R3-MYB gene family in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.).BMC Genomics. 2022 Jun 9;23(1):432. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08658-7. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35681121 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the ftsH protein family and its response to abiotic stress in Nicotiana tabacum L.BMC Genomics. 2022 Jul 12;23(1):503. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08719-x. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35831784 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of Hsp70 gene family in Nicotiana tabacum.Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Apr;46(2):1941-1954. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-04644-7. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30710231
-
Systematic analysis of the non-specific lipid transfer protein gene family in Nicotiana tabacum reveal its potential roles in stress responses.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2022 Feb 1;172:33-47. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.01.002. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35016104 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the root-rhizosphere environment of perennial wheat: a metabolomic perspective.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jul 22;25(1):942. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-07008-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40691757 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the ADH gene family in Artemisia annua L. under UV-B stress.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Mar 19;16:1533225. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1533225. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40177011 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and evolutionary comparative analysis of the DIR gene family in Nicotiana tabacum L. and Solanum tuberosum L.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jul 5;25(1):671. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10577-8. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38970011 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

