Development and validation of a clinical prediction model for the risk of distal metastasis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a real-world study
- PMID: 38166611
- PMCID: PMC10759461
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-023-03084-9
Development and validation of a clinical prediction model for the risk of distal metastasis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a real-world study
Abstract
Background: Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a highly malignant and easily metastatic bile duct tumor with poor prognosis. We aimed at studying the associated risk factors affecting distal metastasis of CCA and using nomogram to guide clinicians in predicting distal metastasis of CCA.
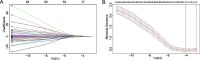
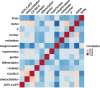
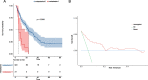
Methods: Based on inclusion and exclusion criteria, 345 patients with CCA were selected from the Fifth Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital and were divided into distal metastases (N = 21) and non-distal metastases (N = 324). LASSO regression models were used to screen for relevant parameters and to compare basic clinical information between the two groups of patients. Risk factors for distal metastasis were identified based on the results of univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses. The nomogram was established based on the results of multivariate logistic regression, and we drawn the corresponding correlation heat map. The predictive accuracy of the nomogram was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and calibration plots. The utility of the model in clinical applications was illustrated by applying decision curve analysis (DCA), and overall survival(OS) analysis was performed using the method of Kaplan-meier.
Results: This study identified 4 independent risk factors for distal metastasis of CCA, including CA199, cholesterol, hypertension and margin invasion, and developed the nomogram based on this. The result of validation showed that the model had significant accuracy for diagnosis with the area under ROC (AUC) of 0.882 (95% CI: 0.843-0.914). Calibration plots and DCA showed that the model had high clinical utility.
Conclusions: This study established and validated a model of nomogram for predicting distal metastasis in patients with CCA. Based on this, it could guide clinicians to make better decisions and provide more accurate prognosis and treatment for patients with CCA.
Keywords: Cholangiocarcinoma; Distal metastasis; Nomogram; Prediction model; Risk factor.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Establishment and external validation of prognosis prediction nomogram for patients with distant metastatic intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: based on a large population.BMC Cancer. 2024 Feb 16;24(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-11976-6. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38365630 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a prediction model for postoperative prognosis in patients with resectable cholangiocarcinoma based on silence information regulator 2 expression.Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Dec 5;53(1):98-107. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2023-0413. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 38105682 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic nomograms for newly diagnosed intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with brain metastasis: A population-based analysis.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022 Sep;247(18):1657-1669. doi: 10.1177/15353702221113828. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022. PMID: 35946168 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of Distant Metastasis and Prognosis in Newly Diagnosed T1 Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Jan 17;2023:6638755. doi: 10.1155/2023/6638755. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36704724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk factors for intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Hepatol. 2020 Jan;72(1):95-103. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.09.007. Epub 2019 Sep 16. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31536748
Cited by
-
Clinical Impact of Caudate Lobectomy in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Involving the Hepatic Hilus.Gut Liver. 2025 May 15;19(3):301-302. doi: 10.5009/gnl250198. Gut Liver. 2025. PMID: 40356325 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Construction of a nomogram for predicting HNSCC distant metastasis and identification of EIF5A as a hub gene.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 11;14(1):13367. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64197-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38862693 Free PMC article.
-
Locus-specific HERV expression associated with hepatocellular carcinoma.Mob DNA. 2025 Jul 16;16(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s13100-025-00367-8. Mob DNA. 2025. PMID: 40671054 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term and Long-term Clinical Outcomes of Combined Caudate Lobectomy for Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Involving the Hepatic Hilus: A Propensity Score Analysis.Gut Liver. 2025 May 15;19(3):438-453. doi: 10.5009/gnl240158. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Gut Liver. 2025. PMID: 39327842 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang H, et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis and surgical management. Cancer Lett. 2015:S0304383515005881. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

