Identification of potential biological processes and key genes in diabetes-related stroke through weighted gene co-expression network analysis
- PMID: 38166912
- PMCID: PMC10762844
- DOI: 10.1186/s12920-023-01752-z
Identification of potential biological processes and key genes in diabetes-related stroke through weighted gene co-expression network analysis
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is an established risk factor for acute ischemic stroke (AIS). Although there are reports on the correlation of diabetes and stroke, data on its pathogenesis is limited. This study aimed to explore the underlying biological mechanisms and promising intervention targets of diabetes-related stroke.
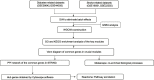
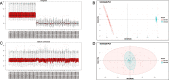
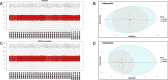
Methods: Diabetes-related datasets (GSE38642 and GSE44035) and stroke-related datasets (GSE16561 and GSE22255) were obtained from the Gene Expression omnibus (GEO) database. The key modules for stroke and diabetes were identified by weight gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA). Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes Genomes (KEGG) analyses were employed in the key module. Genes in stroke- and diabetes-related key modules were intersected to obtain common genes for T2DM-related stroke. In order to discover the key genes in T2DM-related stroke, the Cytoscape and protein-protein interaction (PPI) network were constructed. The key genes were functionally annotated in the Reactome database.
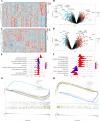
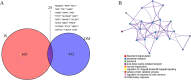
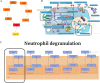
Results: By intersecting the diabetes- and stroke-related crucial modules, 24 common genes for T2DM-related stroke were identified. Metascape showed that neutrophil extracellular trap formation was primarily enriched. The hub gene was granulin precursor (GRN), which had the highest connectivity among the common genes. In addition, functional enrichment analysis indicated that GRN was involved in neutrophil degranulation, thus regulating neutrophil extracellular trap formation.
Conclusions: This study firstly revealed that neutrophil extracellular trap formation may represent the common biological processes of diabetes and stroke, and GRN may be potential intervention targets for T2DM-related stroke.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Diabetes; Neutrophil extracellular trap formation (NETs); Stroke; Weight gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA).
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis to Identify Potential Biological Processes and Key Genes in COVID-19-Related Stroke.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 May 9;2022:4526022. doi: 10.1155/2022/4526022. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35557984 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic analysis for potential biological processes and key targets of heart failure-related stroke.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2021 Sept 15;22(9):718-732. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2000544. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2021. PMID: 34514752 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Up-Regulated ANXA3 Resulting in Fracture Non-Union in Patients With T2DM.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 24;13:890941. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.890941. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35813617 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Shared Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus via Co-expression Networks Analysis.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2020;17(6):566-575. doi: 10.2174/1567205017666200810164932. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2020. PMID: 32781959
-
STAT4 and COL1A2 are potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for heart failure comorbided with depression.Brain Res Bull. 2022 Jun 15;184:68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.03.014. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Brain Res Bull. 2022. PMID: 35367598 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparing gene-gene co-expression network approaches for the analysis of cell differentiation and specification on scRNAseq data.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025 Jun 6;27:2747-2756. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.05.040. eCollection 2025. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 40673123 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Delling FN, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2020 update: a report from the american heart association. Circulation. 2020;141(9):e139–e596. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000757. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

