Effects of manual lymphatic drainage on total knee replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 38167036
- PMCID: PMC10763325
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-023-07153-8
Effects of manual lymphatic drainage on total knee replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Total knee joint replacement (TKR) is an effective method for the treatment of severe knee osteoarthritis. With an increasing number of surgeries, complications such as lower limb edema, pain, and limited mobility have caused a heavy burden. Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) may be a solution to solve the problem. The study aims to evaluate the efficacy of MLD in reducing knee edema, pain, and improving range of motion (ROM) in patients after TKR.
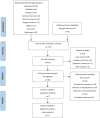
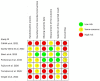
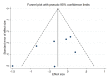
Methods: A search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, CNKI, VIPs, WanFang database, and Google Scholar from inception to June 2023. Only randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared the effects of MLD and non-MLD (or another physiotherapy) on improving knee edema, pain, and ROM after TKR were included. Stata 16.0 was used for meta-analysis. GRADE was used to assess the quality of evidence.
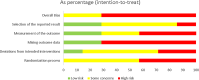
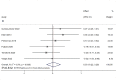
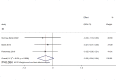
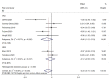
Results: In total, 7 RCTs with 285 patients were identified. There were no significant differences found in the ROM of knee flexion (standardized mean difference (SMD) = 0.03, 95% confidence interval (CI): -0.22, 0.28, P = 0.812) and the ROM of knee extension (SMD= -0.30, 95%CI: -0.64, 0.04, P = 0.084). No differences were observed in the lower extremity circumference after TKR (SMD= -0.09, 95%CI: -0.27, 0.09, P = 0.324). For postoperative pain, there was no significant advantage between the MLD and non-MLD groups (SMD= -0.33, 95%CI: -0.71, 0.04, P = 0.083).
Conclusions: Based on the current evidence from RCTs, manual lymphatic drainage is not recommended for the rehabilitation of patients following total knee replacement.
Keywords: Edema; Manual lymphatic drainage; Pain; Range of motion; Total knee replacement.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Manual lymphatic drainage and Kinesio taping applications reduce early-stage lower extremity edema and pain following total knee arthroplasty.Physiother Theory Pract. 2023 Aug 3;39(8):1582-1590. doi: 10.1080/09593985.2022.2044422. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Physiother Theory Pract. 2023. PMID: 35291929
-
Level I of evidence does not support manual lymphatic drainage for total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 12;13(1):22024. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49291-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38086979 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of lower-limb active resistance exercise on mobility, physical function, knee strength and pain intensity in patients with total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Sep 12;25(1):730. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07845-9. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39267026 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Manual Lymphatic Drainage After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016 May;97(5):674-82. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2016.01.006. Epub 2016 Jan 30. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016. PMID: 26829760 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Postoperative Kinesio Taping on Knee Edema, Pain, and Range of Motion After Total Knee Arthroplasty and Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.JBJS Rev. 2024 Mar 15;12(3). doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.23.00221. eCollection 2024 Mar 1. JBJS Rev. 2024. PMID: 38489396
Cited by
-
Comparative Recovery After Acute Lower-Limb Wounds Treated with Negative-Pressure Wound Therapy and Three Gradations of Manual Rehabilitation.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Jun 23;13(13):1496. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13131496. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40648523 Free PMC article.
-
Demonstration of the effectiveness of complete decongestive treatment in secondary lymphedema developing after total knee arthroplasty.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2024 Dec 23;35(1):45. doi: 10.1007/s00590-024-04167-3. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2024. PMID: 39714522
-
Effectiveness of kinesiotaping for lymphatic drainage after bilateral total knee arthroplasty: A randomized controlled trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Apr 11;104(15):e41971. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041971. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40228285 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Postoperative swelling: influence of a negative pressure application in comparison to manual lymphatic drainage after total knee arthroplasty-a randomized controlled trial.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2025 May 18;35(1):202. doi: 10.1007/s00590-025-04313-5. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2025. PMID: 40382759 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

