The effect of preoperative different dexamethasone regimens on postoperative glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus undergoing total joint arthroplasty: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 38167107
- PMCID: PMC10763206
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-023-04485-y
The effect of preoperative different dexamethasone regimens on postoperative glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus undergoing total joint arthroplasty: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Concerns have been raised regarding the impact of preoperative intravenous dexamethasone on postoperative glycemic control in diabetic patients undergoing total joint arthroplasty (TJA). This study aimed to determine relationships between preoperative different dexamethasone regimens and postoperative fasting blood glucose (FBG), as well as to identify risk factors for postoperative FBG ≥ 200 mg/dl in diabetic patients undergoing TJA.
Methods: This retrospective study included 1216 diabetic patients undergoing TJA and categorized into group A (dexamethasone = 0 mg), group B (dexamethasone = 5 mg), and group C (dexamethasone = 10 mg). All dexamethasone was administered before skin incision. FBG levels were monitored until postoperative day (POD) 3. Analyses were conducted for periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) and wound complications during 90 days postoperatively. And the risk factors for postoperative FBG ≥ 200 mg/dl were identified.
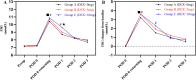
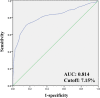
Results: Preoperative dexamethasone administration resulted in a transiently higher FBG on POD 0 and POD 1 (all P < 0.001). However, no differences were observed on POD 2 (P = 0.583) and POD 3 (P = 0.131) among three groups. While preoperative dexamethasone led to an increase in postoperative mean FBG and postoperative maximum FBG (all P < 0.001), no differences were found in wound complications (P = 0.548) and PJI (P = 1.000). Increased HbA1c and preoperative high FBG, but not preoperative dexamethasone, were identified as risk factors for postoperative FBG ≥ 200 mg/dl. Preoperative HbA1c level of ≥ 7.15% was associated with an elevated risk of postoperative FBG ≥ 200 mg/dl.
Conclusions: Although preoperative intravenous administration of 5 mg or 10 mg dexamethasone in diabetic patients showed transient effects on postoperative FBG after TJA, no differences were found in the rates of PJI and wound complications during 90 days postoperatively. Notably, patients with a preoperative HbA1c level of ≥ 7.15% and elevated preoperative FBG may encountered postoperative FBG ≥ 200 mg/dl.
Keywords: Dexamethasone; Diabetes mellitus; Glycemic control; Total joint arthroplasty.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Dexamethasone on Postoperative Glycemic Control in Patients After Primary Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial.J Arthroplasty. 2024 Sep;39(9):2213-2220. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2024.04.030. Epub 2024 Apr 12. J Arthroplasty. 2024. PMID: 38614358 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of a split-dose intravenous dexamethasone and a single high-dose on postoperative blood glucose after total joint arthroplasty: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Jul 2;19(1):388. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04887-6. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38956678 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Intravenous Dexamethasone on Glycemic Control in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus After Total Knee Arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2021 Dec;36(12):3909-3914. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2021.07.021. Epub 2021 Aug 8. J Arthroplasty. 2021. PMID: 34446328
-
Inadequate Glycemic Control Is Associated With Increased Surgical Site Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Arthroplasty. 2018 Jul;33(7):2312-2321.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2018.02.020. Epub 2018 Feb 21. J Arthroplasty. 2018. PMID: 29605149
-
Tobacco Use and Risk of Wound Complications and Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Primary Total Joint Arthroplasty Procedures.J Arthroplasty. 2019 Feb;34(2):385-396.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2018.09.089. Epub 2018 Oct 9. J Arthroplasty. 2019. PMID: 30385090
References
-
- Tien M, Gan TJ, Dhakal I, White WD, Olufolabi AJ, Fink R, et al. The effect of anti-emetic doses of dexamethasone on postoperative blood glucose levels in non-diabetic and diabetic patients: a prospective randomised controlled study. Anaesthesia. 2016;71(9):1037–1043. doi: 10.1111/anae.13544. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

