Causal relationship between systemic lupus erythematosus and primary liver cirrhosis based on two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization and transcriptome overlap analysis
- PMID: 38167341
- PMCID: PMC10762944
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-023-03235-z
Causal relationship between systemic lupus erythematosus and primary liver cirrhosis based on two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization and transcriptome overlap analysis
Abstract
Background: Overlapping cases of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) are rare and have not yet been fully proven to be accidental or have a common genetic basis.
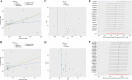
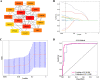
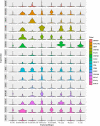
Methods: Two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis was applied to explore the potential causal relationship between SLE and PBC. The heterogeneity and reliability of MR analysis were evaluated through Cochran's Q-test and sensitivity test, respectively. Next, transcriptome overlap analysis of SLE and PBC was performed using the Gene Expression Omnibus database to identify the potential mechanism of hub genes. Finally, based on MR analysis, the potential causal relationship between hub genes and SLE or PBC was validated again.
Results: The MR analysis results indicated that SLE and PBC were both high-risk factors for the occurrence and development of the other party. On the one hand, MR analysis had heterogeneity, and on the other hand, it also had robustness. Nine hub genes were identified through transcriptome overlap analysis, and machine learning algorithms were used to verify their high recognition efficiency for SLE patients. Finally, based on MR analysis, it was verified that there was no potential causal relationship between the central gene SOCS3 and SLE, but it was a high-risk factor for the potential risk of PBC.
Conclusion: The two-sample bidirectional MR analysis revealed that SLE and PBC were high-risk factors for each other, indicating that they had similar genetic bases, which could to some extent overcome the limitation of insufficient overlap in case samples of SLE and PBC. The analysis of transcriptome overlapping hub genes provided a theoretical basis for the potential mechanisms and therapeutic targets of SLE with PBC overlapping cases.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; Primary biliary cirrhosis; Systemic lupus erythematosus; Transcriptome overlap analysis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang L, Yu C, Ren C. Systemic lupus erythematosus combined with Evans syndrome and primary biliary cirrhosis: a rare case report. Asian J Surg. 2023;S1015–9584(23):00850–3. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

