TC2N inhibits distant metastasis and stemness of breast cancer via blocking fatty acid synthesis
- PMID: 38167440
- PMCID: PMC10763294
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-023-04721-3
TC2N inhibits distant metastasis and stemness of breast cancer via blocking fatty acid synthesis
Abstract
Background: Tandem C2 domains, nuclear (TC2N) is a C2 domain-containing protein that belongs to the carboxyl-terminal type (C-type) tandem C2 protein family, and acts as an oncogenic driver in several cancers. Previously, we preliminarily reported that TC2N mediates the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway to inhibit tumor growth of breast cancer (BC) cells. Beyond that, its precise biological functions and detailed molecular mechanisms in BC development and progression are not fully understood.
Methods: Tumor tissues of 212 BC patients were subjected to tissue microarray and further assessed the associations of TC2N expression with pathological parameters and FASN expression. The protein levels of TC2N and FASN in cell lines and tumor specimens were monitored by qRT-PCR, WB, immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry. In vitro cell assays, in vivo nude mice model was used to assess the effect of TC2N ectopic expression on tumor metastasis and stemness of breast cancer cells. The downstream signaling pathway or target molecule of TC2N was mined using a combination of transcriptomics, proteomics and lipidomics, and the underlying mechanism was explored by WB and co-IP assays.
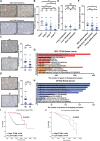
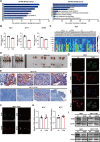
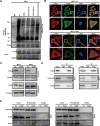
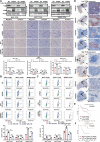
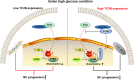
Results: Here, we found that the expression of TC2N remarkedly silenced in metastatic and poorly differentiated tumors. Function-wide, TC2N strongly inhibits tumor metastasis and stem-like properties of BC via inhibition of fatty acid synthesis. Mechanism-wise, TC2N blocks neddylated PTEN-mediated FASN stabilization by a dual mechanism. The C2B domain is crucial for nuclear localization of TC2N, further consolidating the TRIM21-mediated ubiquitylation and degradation of FASN by competing with neddylated PTEN for binding to FASN in nucleus. On the other hand, cytoplasmic TC2N interacts with import proteins, thereby restraining nuclear import of PTEN to decrease neddylated PTEN level.
Conclusions: Altogether, we demonstrate a previously unidentified role and mechanism of TC2N in regulation of lipid metabolism and PTEN neddylation, providing a potential therapeutic target for anti-cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Cancer stem cell; Fatty synthesis; Metastasis; PTEN neddylation; TC2N.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TC2N maintains stem cell-like characteristics to accelerate lung carcinogenesis by blockade of dual specificity protein phosphatase 3.Cell Biosci. 2025 Jan 23;15(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13578-025-01348-3. Cell Biosci. 2025. PMID: 39849581 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of TC2N as a novel promising suppressor of PI3K-AKT signaling in breast cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2019 May 29;10(6):424. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1663-5. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31142739 Free PMC article.
-
PTENP1/miR-20a/PTEN axis contributes to breast cancer progression by regulating PTEN via PI3K/AKT pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 13;38(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1260-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31196157 Free PMC article.
-
Neddylation of PTEN regulates its nuclear import and promotes tumor development.Cell Res. 2021 Mar;31(3):291-311. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-00443-z. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 33299139 Free PMC article.
-
Small in Size, but Large in Action: microRNAs as Potential Modulators of PTEN in Breast and Lung Cancers.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 18;11(2):304. doi: 10.3390/biom11020304. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33670518 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fatty Acid Synthase-Derived Lipid Stores Support Breast Cancer Metastasis.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 5:rs.3.rs-5510550. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5510550/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Cancer Metab. 2025 Jul 10;13(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s40170-025-00404-3. PMID: 39678343 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
TC2N promotes the proliferation and invasion of head and neck cancer cells with the p53-R175H.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Jul 30;14(7):3905-3919. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-2130. Epub 2025 Jul 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40792159 Free PMC article.
-
Inverse FASN and LDHA correlation drives metabolic resistance in breast cancer.J Transl Med. 2024 Jul 24;22(1):676. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05517-9. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39044184 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty acid synthase-derived lipid stores support breast cancer metastasis.Cancer Metab. 2025 Jul 10;13(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s40170-025-00404-3. Cancer Metab. 2025. PMID: 40640944 Free PMC article.
-
TC2N maintains stem cell-like characteristics to accelerate lung carcinogenesis by blockade of dual specificity protein phosphatase 3.Cell Biosci. 2025 Jan 23;15(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13578-025-01348-3. Cell Biosci. 2025. PMID: 39849581 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

