A novel PDPN antagonist peptide CY12-RP2 inhibits melanoma growth via Wnt/β-catenin and modulates the immune cells
- PMID: 38167452
- PMCID: PMC10759609
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-023-02910-y
A novel PDPN antagonist peptide CY12-RP2 inhibits melanoma growth via Wnt/β-catenin and modulates the immune cells
Abstract
Background: Podoplanin (PDPN) is a highly conserved, mucin-type protein specific to the lymphatic system. Overexpression of PDPN is associated with the progression of various solid tumors, and plays an important roles in the tumor microenvironment by regulating the immune system. However, the role of PDPN-mediated signal activation in the progression of melanoma is still unknown.
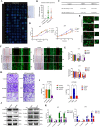
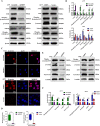
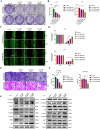
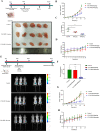
Methods: PDPN expression was first analyzed in 112 human melanoma tissue microarrays and melanoma cell lines. Functional experiments including proliferation, clone formation, migration, and metastasis were utilized to identify the suppressive effects of PDPN. The Ph.D.TM-12 Phage Display Peptide Library was used to obtain a PDPN antagonist peptide, named CY12-RP2. The immunofluorescence, SPR assay, and flow cytometry were used to identify the binding specificity of CY12-RP2 with PDPN in melanoma cells. Functional and mechanistic assays in vivo and in vitro were performed for discriminating the antitumor and immune activation effects of CY12-RP2.
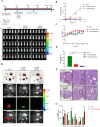
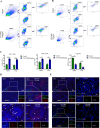
Results: PDPN was overexpressed in melanoma tissue and cells, and inhibited melanoma cells proliferation, migration, and metastasis by blocking the EMT and Wnt/β-catenin pathway. PDPN antagonistic peptide, CY12-RP2, could specifically bind with PDPN, suppressing melanoma various functions inducing apoptosis in both melanoma cells and 3D spheroids. CY12-RP2 also enhanced the anti-tumor capacity of PBMC, and inhibited melanoma cells growth both in xenografts and allogeneic mice model. Moreover, CY12-RP2 could inhibit melanoma lung metastasis, and abrogated the immunosuppressive effects of PDPN by increasing the proportion of CD3 + CD4 + T cells, CD3 + CD8 + T cells, CD49b + Granzyme B + NK cells, and CD11b + CD86 + M1-like macrophages and the levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, and IFN-γ.
Conclusions: This study has demonstrated the important role of PDPN in the progression of melanoma and formation of immunosuppressive environment, and provided a potential approach of treating melanoma using the novel CY12-RP2 peptide. In melanoma, PDPN is overexpressed in the cancer cells, and promotes melanoma cells growth and metastasis through activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Treatment with the PDPN antagonistic peptide CY12-RP2 could not only inhibit the melanoma growth and metastasis both in vitro and in vivo through Wnt/β-catenin pathway blockade, but also abrogate the immunosuppressive effects of PDPN through modulating immune cells.
Keywords: CY12-RP2 peptide; EMT; Immune activation; Melanoma; PDPN; Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sodium thiosulfate inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in melanoma via regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.J Dermatol Sci. 2023 Feb;109(2):89-98. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2023.02.002. Epub 2023 Feb 14. J Dermatol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36870927
-
CUL4B promotes metastasis and proliferation in pancreatic cancer cells by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Jul;119(7):5308-5323. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26643. Epub 2018 Mar 14. J Cell Biochem. 2018. Retraction in: J Cell Biochem. 2021 Nov;122 Suppl 1:S89. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30057. PMID: 29274277 Retracted.
-
Podoplanin regulates mammary stem cell function and tumorigenesis by potentiating Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Development. 2018 Feb 21;145(4):dev160382. doi: 10.1242/dev.160382. Development. 2018. PMID: 29361573
-
Roles of Podoplanin in Malignant Progression of Tumor.Cells. 2022 Feb 7;11(3):575. doi: 10.3390/cells11030575. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathological role of long non-coding (lnc) RNA in the regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway during epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT).Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Aug;248:154566. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154566. Epub 2023 May 24. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37285735 Review.
Cited by
-
TCF7 enhances pulmonary hypertension by boosting stressed natural killer cells and their interaction with pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells.Respir Res. 2025 May 29;26(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s12931-025-03276-9. Respir Res. 2025. PMID: 40442690 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting pathogenic fibroblast-like synoviocyte subsets in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 May 23;26(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03343-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38783357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CAF Specific Expression of Podoplanin May Be Dispensable for the Malignancy of Malignant Melanoma.Mol Carcinog. 2025 Feb;64(2):215-220. doi: 10.1002/mc.23841. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Mol Carcinog. 2025. PMID: 39513649 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the breast cancer tumor microenvironment: crucial factors influencing natural killer cell function and therapeutic strategies.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Mar 24;21(6):2606-2628. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.108803. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40303301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N7-methyladenosine-induced SLC7A7 serves as a prognostic biomarker in pan-cancer and promotes CRC progression in colorectal cancer.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):30755. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80885-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39730571 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

