Exosome-mediated delivery of super-repressor IκBα alleviates inflammation and joint damages in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 38167497
- PMCID: PMC10759503
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-023-03225-1
Exosome-mediated delivery of super-repressor IκBα alleviates inflammation and joint damages in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: This study aims to investigate the potential anti-inflammatory effects of exosomes engineered to carry super-repressor IκB (Exo-srIκB), an exosome-based NF-κB inhibitor, in the context of RA.
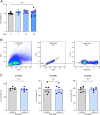
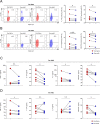
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and synovial fluid mononuclear cells (SFMCs) were collected from patients diagnosed with RA and treated with Exo-srIκB to test the therapeutic potential. Flow cytometry analysis was performed to assess the production of inflammatory cytokines (IL-17A and GM-CSF) by the cells. ELISA was utilized to measure the levels of TNF-α, IL-17A, IL-6, and GM-CSF. Arthritis was induced in SKG mice by intraperitoneal injection of curdlan. DBA/1 J mice were used in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) experiments. After the development of arthritis, mice were injected with either Exo-Naïve (control exosome) or Exo-srIκB. Arthritis scores were recorded biweekly, and histological observations of the ankle joint were conducted using H&E and safranin-O staining. Additionally, bone erosion was evaluated using micro-CT imaging.
Results: In the ex vivo study involving human PBMCs and SFMCs, treatment with Exo-srIκB demonstrated a notable reduction in inflammatory cytokines. Furthermore, in both the SKG and CIA models, Exo-srIκB treatment exhibited significant reductions in inflammation, cartilage destruction, and bone erosion within the joint tissues when compared to the Exo-Naive control group. Additionally, the radiographic score assessed through microCT showed a significant decrease compared to the Exo-Naive control group.
Conclusion: Overall, these findings suggest that Exo-srIκB possesses anti-inflammatory properties in human RA cells and animal models, making it a promising therapeutic candidate for the treatment of RA.
Keywords: Exosome; Inflammation; NF-κB; Rheumatoid arthritis; Treatment.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Chulhee Choi is the founder and shareholder, and So-Hee Ahn, Cheolhyoung Park, and Jae-Kwang Yoo are minor shareholders of ILIAS Biologics Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Complementary action of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-17A induces interleukin-23, receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand, and matrix metalloproteinases and drives bone and cartilage pathology in experimental arthritis: rationale for combination therapy in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Jun 17;17(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0683-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26081345 Free PMC article.
-
Protection against cartilage and bone destruction by systemic interleukin-4 treatment in established murine type II collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Res. 1999;1(1):81-91. doi: 10.1186/ar14. Epub 1999 Oct 26. Arthritis Res. 1999. PMID: 11056663 Free PMC article.
-
Wedelolactone ameliorates synovial inflammation and cardiac complications in a murine model of collagen-induced arthritis by inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome activation.Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2022;60(4):301-310. doi: 10.5603/FHC.a2022.0025. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2022. PMID: 36380683
-
Activation of TGR5 alleviates inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis peripheral blood mononuclear cells and in mice with collagen II‑induced arthritis.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Nov;20(5):4540-4550. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10711. Epub 2019 Sep 26. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31702035 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells primed with disease-condition-serum improved therapeutic efficacy in a mouse rheumatoid arthritis model via enhanced TGF-β1 production.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Oct 4;14(1):283. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03523-0. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37794417 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exosomes in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases: Recent Advances in Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Applications.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Apr 21;20:5137-5160. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S506221. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40292402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles as therapeutic agents in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review of current evidence.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Mar;33(3):889-915. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01670-9. Epub 2025 Mar 1. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40024954
-
Exosomes in Action: Unraveling Their Role in Autoimmune Diseases and Exploring Potential Therapeutic Applications.Immune Netw. 2024 Feb 20;24(2):e12. doi: 10.4110/in.2024.24.e12. eCollection 2024 Apr. Immune Netw. 2024. PMID: 38725675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles: immunomodulation, diagnosis, and promising therapeutic roles for rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 18;15:1499929. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1499929. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39624102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes in inflammation and cancer: from bench to bedside applications.Mol Biomed. 2025 Jun 10;6(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s43556-025-00280-9. Mol Biomed. 2025. PMID: 40490663 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- NejatbakhshSamimi L, Farhadi E, Tahmasebi MN, Jamshidi A, SharafatVaziri A, Mahmoudi M. NF-κB signaling in rheumatoid arthritis with focus on fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Autoimmun Highlights. 2020;11(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13317-020-00135-z. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

