Sequential immunotherapy and targeted therapy for metastatic BRAF V600 mutated melanoma: 4-year survival and biomarkers evaluation from the phase II SECOMBIT trial
- PMID: 38167503
- PMCID: PMC10761671
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-44475-6
Sequential immunotherapy and targeted therapy for metastatic BRAF V600 mutated melanoma: 4-year survival and biomarkers evaluation from the phase II SECOMBIT trial
Abstract
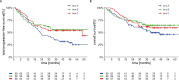
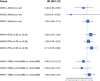
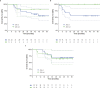
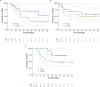
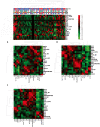
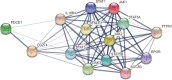
No prospective data were available prior to 2021 to inform selection between combination BRAF and MEK inhibition versus dual blockade of programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) as first-line treatment options for BRAFV600-mutant melanoma. SECOMBIT (NCT02631447) was a randomized, three-arm, noncomparative phase II trial in which patients were randomized to one of two sequences with immunotherapy or targeted therapy first, with a third arm in which an 8-week induction course of targeted therapy followed by a planned switch to immunotherapy was the first treatment. BRAF/MEK inhibitors were encorafenib plus binimetinib and checkpoint inhibitors ipilimumab plus nivolumab. Primary outcome of overall survival was previously reported, demonstrating improved survival with immunotherapy administered until progression and followed by BRAF/MEK inhibition. Here we report 4-year survival outcomes, confirming long-term benefit with first-line immunotherapy. We also describe preliminary results of predefined biomarkers analyses that identify a trend toward improved 4-year overall survival and total progression-free survival in patients with loss-of-function mutations affecting JAK or low baseline levels of serum interferon gamma (IFNy). These long-term survival outcomes confirm immunotherapy as the preferred first-line treatment approach for most patients with BRAFV600-mutant metastatic melanoma, and the biomarker analyses are hypothesis-generating for future investigations of predictors of durable benefit with dual checkpoint blockade and targeted therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing interests: P.A.A.: Stock and Other Ownership Interests: PrimeVax. Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche/Genentech, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Array BioPharma, Merck Serono, Pierre Fabre, Incyte, MedImmune, AstraZeneca, Sun Pharma, Sanofi, Idera, Ultimovacs, Sandoz, Immunocore, 4SC, Alkermes, Italfarmaco, Nektar, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eisai, Regeneron, Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, OncoSec, Nouscom, Takis Biotech, Lunaphore Technologies, Seattle Genetics, ITeos Therapeutics, Medicenna, Bio-Al Health, ValoTx. Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Roche/Genentech (Inst), Array BioPharma (Inst), Sanofi (Inst), Pfizer (Inst). Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer. M.M. Honoraria: MSD Oncology, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi/Aventis, Bristol Myers Squibb/Sanofi. Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD Oncology, Novartis, Pierre Fabre. Research Funding: Novartis (Inst). Pier Francesso Ferrucci. Expert Testimony: Delcath Systems. M.G. Consulting or Advisory Role: BMS, Novartis, Pierre Fabre. Speakers’ Bureau: BMS, Novartis, Pierre Fabre. Research Funding: MSD. P.R. Honoraria: Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD, Novartis, Roche, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi, Merck. Consulting or Advisory Role: Novartis, Blueprint Medicines, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pierre Fabre, MSD, Amgen. Speakers’ Bureau: Pfizer, Novartis, Pierre Fabre. Research Funding: Novartis (Inst), Roche (Inst), Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst). Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Orphan Europe, Pierre Fabre. V.F. Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis. Speakers’ Bureau: Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, MSD Oncology. A.A. Consulting or Advisory Role: BMS, Roche, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, MSD, Merck, Sanofi. Speakers’ Bureau: Pierre Fabre, Novartis, MSD, BMS, Roche, Merck, Sanofi. Research Funding: Pierre Fabre (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Roche (Inst), BMS (Inst), MSD (Inst), Merck (Inst), Sanofi (Inst). Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: BMS, MSD, Novartis, Pierre Fabre. H.G. Honoraria: Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD Oncology, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi/Regeneron. Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD Oncology, Amgen, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi/Regeneron. Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Roche (Inst), MSD Oncology (Inst), Amgen (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Iovance Biotherapeutics (Inst). Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD, Amgen, Pfizer. E.R. Honoraria: Amgen, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp Dohme, Merck, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Sanofi. Consulting or Advisory Role: Amgen, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Merck, Novartis, Pierre Fabre. Speakers’ Bureau: Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Merck, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi. Research Funding: Amgen (Inst), Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Merck Sharp & Dohme (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Pierre Fabre (Inst), Roche (Inst), Cure. The remaining authors declare no other competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

