Beyond invasive biopsies: using VASARI MRI features to predict grade and molecular parameters in gliomas
- PMID: 38167551
- PMCID: PMC10759759
- DOI: 10.1186/s40644-023-00638-8
Beyond invasive biopsies: using VASARI MRI features to predict grade and molecular parameters in gliomas
Abstract
Background: Gliomas present a significant economic burden and patient management challenge. The 2021 WHO classification incorporates molecular parameters, which guide treatment decisions. However, acquiring these molecular data involves invasive biopsies, prompting a need for non-invasive diagnostic methods. This study aims to assess the potential of Visually AcceSAble Rembrandt Images (VASARI) MRI features to predict glioma characteristics such as grade, IDH mutation, and MGMT methylation status.
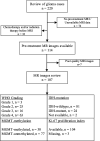
Methods: This study enrolled 107 glioma patients treated between 2017 and 2022, meeting specific criteria including the absence of prior chemotherapy/radiation therapy, and the presence of molecular and MRI data. Images were assessed using the 27 VASARI MRI features by two blinded radiologists. Pathological and molecular assessments were conducted according to WHO 2021 CNS Tumor classification. Cross-validation Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (CV-LASSO) logistic regression was applied for statistical analysis to identify significant VASARI features in determining glioma grade, IDH mutation, and MGMT methylation status.
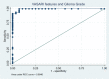
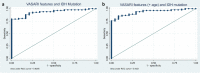
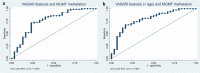
Results: The study demonstrated substantial observer agreement in VASARI feature evaluation (inter- and intra-observer κ = 0.714 - 0.831 and 0.910, respectively). Patient imaging characteristics varied significantly with glioma grade, IDH mutation, and MGMT methylation. A predictive model was established using VASARI features for glioma grade prediction, exhibiting an AUC of 0.995 (95% CI = 0.986 - 0.998), 100% sensitivity, and 92.86% specificity. IDH mutation status was predicted with AUC 0.930 (95% CI = 0.882 - 0.977), and improved slightly to 0.933 with 'age-at-diagnosis' added. A model predicting MGMT methylation had a satisfactory performance (AUC 0.757, 95% CI = 0.645 - 0.868), improving to 0.791 when 'age-at-diagnosis' was added.
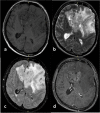
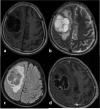
Conclusions: The T1/FLAIR ratio, enhancement quality, hemorrhage, and proportion enhancing predict glioma grade with excellent accuracy. The proportion enhancing, thickness of enhancing margin, and T1/FLAIR ratio are significant predictors for IDH mutation status. Lastly, MGMT methylation is related to the longest diameter of the lesion, edema crossing the midline, and the proportion of the non-enhancing lesion. VASARI MRI features offer non-invasive and accurate predictive models for glioma grade, IDH mutation, and MGMT methylation status, enhancing glioma patient management.
Keywords: Glioma; Grade; IDH; MGMT; MRI; VASARI.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

