Infliximab Monotherapy vs Combination Therapy for Pediatric Crohn's Disease Exhibit Similar Pharmacokinetics
- PMID: 38167922
- PMCID: PMC12102478
- DOI: 10.1093/ibd/izad307
Infliximab Monotherapy vs Combination Therapy for Pediatric Crohn's Disease Exhibit Similar Pharmacokinetics
Abstract
Background: The use of concomitant azathioprine may improve efficacy and pharmacokinetic (PK) properties of infliximab (IFX) but is also associated with an increased risk of adverse events. Proactive therapeutic drug monitoring (pTDM) of IFX monotherapy is an alternative strategy to improve PK. The aim of this study was to evaluate whether IFX with an immunomodulator (combo) has PK benefits over IFX-pTDM (mono) in pediatric Crohn's disease (CD).
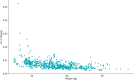
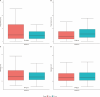
Methods: This PK analysis included pediatric CD patients who started either IFX combo (TISKids study) or IFX mono with pTDM (REFINE cohort). Combo and mono IFX trough levels (TLs) and antibodies-to-infliximab were assessed at infusion 3, 4, and 5. A population PK model was built to compare IFX PK outcomes (clearance [CL], TLs and cumulative exposure) between combo and mono groups at infusion 4 and 5. Clinical response and steroid-free clinical remission (SFCR) was assessed at infusion 4 and 5.
Results: This study included 128 pediatric CD patients (66 mono and 62 combo). At infusion 5, there was no significant difference between mono and combo median TLs 4.1 µg/mL (2.1, 7.8) vs 5.9 µg/mL (3.2, 9.4; P = .14) or median CL 0.26 L/d (0.21, 0.32) vs 0.26 L/d (0.21, 0.33; P = .81). Mono patients had a lower SFCR rate at infusion 5 (53% [31 of 59] vs 80% [32 of 40]; P = .01). Clinical response rates were significantly higher among combo than mono patients at both infusion 4 and 5.
Conclusions: This study suggests that there are no PK differences (TLs and CL) between combo and mono therapy in pediatric CD patients who started IFX.
Keywords: anti-TNF therapy; children; immunomodulator; inflammatory bowel disease; pharmacokinetics.
Plain language summary
This study compared the pharmacokinetics of infliximab combination therapy with azathioprine vs infliximab with proactive therapeutic drug monitoring as monotherapy among pediatric patients with Crohn’s disease within the first 22 weeks. No pharmacokinetic differences were found between monotherapy and combination therapy.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. All rights reserved. For commercial re-use, please contact reprints@oup.com for reprints and translation rights for reprints. All other permissions can be obtained through our RightsLink service via the Permissions link on the article page on our site—for further information please contact journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
L.R.: Collaboration with Abbvie, Lilly, Takeda, Janssen, and Pfizer. R.A.A.M. has received grants from governmental and societal research institutes such as NWO, ZonMW, Dutch Kidney Foundation, and Innovation Fund and unrestricted investigator research grants from Baxter/Baxalta/Shire/Takeda, Bayer, CSL Behring, Sobi, and CelltrionHC. He has served as advisor for Bayer, CSL Behring, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Baxter/Baxalta/Shire/Takeda. All grants and fees paid to the institution. R.C., S.V., J.vL., M.J., M.S., P.M., and G.H. have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of endoscopic healing and durability between combination therapy with infliximab and azathioprine versus infliximab monotherapy in pediatric Crohn's disease.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23025. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06445-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594430 Free PMC article.
-
Proactively Optimized Infliximab Monotherapy Is as Effective as Combination Therapy in IBD.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2019 Jan 1;25(1):134-141. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izy203. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2019. PMID: 29868777
-
Predictors of Infliximab Trough Concentrations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients Using a Repeated-Measures Design.Ther Drug Monit. 2020 Feb;42(1):102-110. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000669. Ther Drug Monit. 2020. PMID: 31283556
-
Pediatric IBD Patients Treated With Infliximab and Proactive Drug Monitoring Benefit From Early Concomitant Immunomodulatory Therapy: A Retrospective Analysis of a 10-Year Real-Life Cohort.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024 Nov 4;30(11):2004-2018. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izad277. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024. PMID: 38011813
-
Reactive Immunomodulator Addition to Infliximab Monotherapy Restores Clinical Response in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Meta-Analysis.Dig Dis Sci. 2024 Oct;69(10):3920-3931. doi: 10.1007/s10620-024-08515-5. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Dig Dis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38877332
Cited by
-
Clinical and Biochemical Factors Associated with Infliximab Pharmacokinetics in Paediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 27;14(3):845. doi: 10.3390/jcm14030845. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39941516 Free PMC article.
-
Considerations in Paediatric and Adolescent Inflammatory Bowel Disease.J Crohns Colitis. 2024 Oct 30;18(Supplement_2):ii31-ii45. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjae087. J Crohns Colitis. 2024. PMID: 39475081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of endoscopic healing and durability between combination therapy with infliximab and azathioprine versus infliximab monotherapy in pediatric Crohn's disease.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23025. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06445-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hyams J, Crandall W, Kugathasan S, et al. ; REACH Study Group. Induction and maintenance infliximab therapy for the treatment of moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease in children. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(3):863-73; quiz 1165-6. - PubMed
-
- van Rheenen PF, Aloi M, Assa A, et al. The medical management of paediatric Crohn’s disease: an ECCO-ESPGHAN guideline update. J Crohns Colitis. 2021;15(2):171-194. - PubMed
-
- Fasanmade AA, Adedokun OJ, Blank M, Zhou H, Davis HM. Pharmacokinetic properties of infliximab in children and adults with Crohn’s disease: a retrospective analysis of data from 2 phase III clinical trials. Clin Ther. 2011;33(7):946-964. - PubMed
-
- Brandse JF, van den Brink GR, Wildenberg ME, et al. Loss of infliximab into feces is associated with lack of response to therapy in patients with severe Ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2015;149(2):350-5.e2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

