SIRT1 as a potential key regulator for mediating apoptosis in oropharyngeal cancer using cyclophosphamide and all-trans retinoic acid
- PMID: 38167952
- PMCID: PMC10761886
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-50478-6
SIRT1 as a potential key regulator for mediating apoptosis in oropharyngeal cancer using cyclophosphamide and all-trans retinoic acid
Abstract
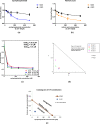
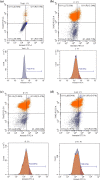
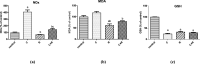
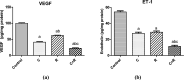
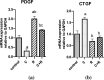
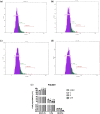
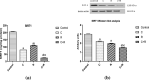
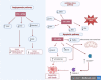
Although cyclophosphamide (CTX) has been used for recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancers, resistance is usually expected. Thus, we conducted this study to examine the effect of adding all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) to CTX, to increase efficacy of CTX and reduce the risk of resistance developed. In this study, we investigated the combined effect of ATRA and CTX on the expression of apoptotic and angiogenesis markers in oropharyngeal carcinoma cell line (NO3), and the possible involved mechanisms. ATRA and CTX in combination significantly inhibited the proliferation of NO3 cells. Lower dose of CTX in combination with ATRA exhibited significant cytotoxicity than that of CTX when used alone, implying lower expected toxicity. Results showed that ATRA and CTX modulated oxidative stress; increased NOx and MDA, reduced GSH, and mRNA expression of Cox-2, SIRT1 and AMPK. Apoptosis was induced through elevating mRNA expressions of Bax and PAR-4 and suppressing that of Bcl-xl and Bcl-2, parallel with increased caspases 3 and 9 and decreased VEGF, endothelin-1 and CTGF levels. The primal action of the combined regimen on inflammatory signaling highlights its impact on cell death in NO3 cell line which was mediated by oxidative stress associated with apoptosis and suppression of angiogenesis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

