Autonomous swab robot for naso- and oropharyngeal COVID-19 screening
- PMID: 38167977
- PMCID: PMC10762007
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-50291-1
Autonomous swab robot for naso- and oropharyngeal COVID-19 screening
Abstract
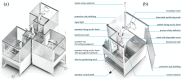
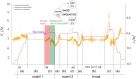
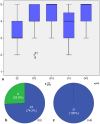
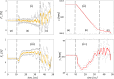
The COVID-19 outbreak has triggered a global health and economic crisis, necessitating widespread testing to control viral spread amidst rising cases and fatalities. The recommended testing method, a combined naso- and oropharyngeal swab, poses risks and demands limited protective gear. In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, we developed and tested the first autonomous swab robot station for Naso- and Oropharyngeal Coronavirus Screening (SR-NOCS). A force-sensitive robot running under a Cartesian impedance controller is employed to drive the swab to the sampling area. This groundbreaking device underwent two clinical studies-one conducted during the initial pandemic lockdown in Europe (early 2021) and the other, more recently, in a public place after the pandemic had subsided earlier in the year 2023. In total, 52 patients suspected of COVID-19 infection were included in these clinical studies. The results revealed a complete positive correlation between autonomous and manual sampling. The test subjects exhibited a high acceptance rate, all expressing a willingness to undergo future tests with SR-NOCS. Based on our findings, such systems could enhance testing capabilities, potentially conducting up to 300 tests per robot per day with consistent precision. The tests can be carried out with minimal supervision, reducing infection risks and effectively safeguarding patients and healthcare workers.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
While conducting the study Simon Haddadin and Sami Haddadin have been minority shareholders of Franka Emika GmbH, while Fabio Tenebruso and Daniel Wahrmann have been employed by Franka Emika GmbH. Dirk Wilhelm, Abdeldjallil Naceri, and Hamid Sabeghian declare to have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Detection from Saliva Sampling and Oropharyngeal Swab.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0142222. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01422-22. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36129278 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of four different strategies for SARS-CoV-2 surveillance in the general population (CoV-Surv Study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a cluster-randomised, two-factorial controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 8;22(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04982-z. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33419461 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Imatinib for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04819-9. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33115543 Free PMC article.
-
Universal screening for SARS-CoV-2 infection: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 15;9(9):CD013718. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013718. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33502003 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 detection in different respiratory sites: A systematic review and meta-analysis.EBioMedicine. 2020 Sep;59:102903. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102903. Epub 2020 Jul 24. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 32718896 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Case study on force compliant robot arm controller for nasopharyngeal swab insertion.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23402. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06032-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40603441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Who coronavirus (covid-19) dashboard. https://who.sprinklr.com/ (2019). Accessed: 2023-08-16.
-
- Covid-19 dashboard by the center for systems science and engineering (csse) at johns hopkins university (jhu). https://gisanddata.maps.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/bda7594.... Accessed: 2023-08-16.
-
- Service, R. F. The standard coronavirus test, if available, works well–but can new diagnostics help in this pandemic? (2022). Accessed on 08 01, 2023.
-
- Normile, D. Coronavirus cases have dropped sharply in south korea,what’s the secret to its success? https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2020/03/coronavirus-cases-have-dropped-s... (2020).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

