Novel molecular mechanism in Malan syndrome uncovered through genome sequencing reanalysis, exon-level Array, and RNA sequencing
- PMID: 38168088
- PMCID: PMC11003828
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.63516
Novel molecular mechanism in Malan syndrome uncovered through genome sequencing reanalysis, exon-level Array, and RNA sequencing
Abstract
The NFIX gene encodes a DNA-binding protein belonging to the nuclear factor one (NFI) family of transcription factors. Pathogenic variants of NFIX are associated with two autosomal dominant Mendelian disorders, Malan syndrome (MIM 614753) and Marshall-Smith syndrome (MIM 602535), which are clinically distinct due to different disease-causing mechanisms. NFIX variants associated with Malan syndrome are missense variants mostly located in exon 2 encoding the N-terminal DNA binding and dimerization domain or are protein-truncating variants that trigger nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) resulting in NFIX haploinsufficiency. NFIX variants associated with Marshall-Smith syndrome are protein-truncating and are clustered between exons 6 and 10, including a recurrent Alu-mediated deletion of exons 6 and 7, which can escape NMD. The more severe phenotype of Marshall-Smith syndrome is likely due to a dominant-negative effect of these protein-truncating variants that escape NMD. Here, we report a child with clinical features of Malan syndrome who has a de novo NFIX intragenic duplication. Using genome sequencing, exon-level microarray analysis, and RNA sequencing, we show that this duplication encompasses exons 6 and 7 and leads to NFIX haploinsufficiency. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of Malan Syndrome caused by an intragenic NFIX duplication.
Keywords: Malan syndrome; NFIX; duplication; overgrowth.
© 2024 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


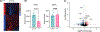
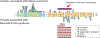
Similar articles
-
Further delineation of Malan syndrome.Hum Mutat. 2018 Sep;39(9):1226-1237. doi: 10.1002/humu.23563. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Hum Mutat. 2018. PMID: 29897170 Free PMC article.
-
NFIX mutations affecting the DNA-binding domain cause a peculiar overgrowth syndrome (Malan syndrome): a new patients series.Eur J Med Genet. 2015 Sep;58(9):488-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2015.06.009. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Eur J Med Genet. 2015. PMID: 26193383
-
Deletions in the 3' part of the NFIX gene including a recurrent Alu-mediated deletion of exon 6 and 7 account for previously unexplained cases of Marshall-Smith syndrome.Hum Mutat. 2014 Sep;35(9):1092-100. doi: 10.1002/humu.22603. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Hum Mutat. 2014. PMID: 24924640
-
Malan syndrome: Sotos-like overgrowth with de novo NFIX sequence variants and deletions in six new patients and a review of the literature.Eur J Hum Genet. 2015 May;23(5):610-5. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2014.162. Epub 2014 Aug 13. Eur J Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 25118028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Malan syndrome (Sotos syndrome 2) in two patients with 19p13.2 deletion encompassing NFIX gene and novel NFIX sequence variant.Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2016 Mar;160(1):161-7. doi: 10.5507/bp.2016.006. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2016. PMID: 26927468 Review.
References
-
- Aggarwal A, Nguyen J, Rivera-Davila M, Rodriguez-Buritica D. 2017. Marshall-Smith syndrome: Novel pathogenic variant and previously unreported associations with precocious puberty and aortic root dilatation. Eur J Med Genet 60(7):391–394. - PubMed
-
- Cope H, Spillmann R, Rosenfeld JA, Brokamp E, Signer R, Schoch K, Kelley EG, Sullivan JA, Macnamara E, Lincoln S, Golden-Grant K, Undiagnosed Diseases N, Orengo JP, Clark G, Burrage LC, Posey JE, Punetha J, Robertson A, Cogan J, Phillips JA 3rd, Martinez-Agosto J, Shashi V. 2020. Missed diagnoses: Clinically relevant lessons learned through medical mysteries solved by the Undiagnosed Diseases Network. Mol Genet Genomic Med 8(10):e1397. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gurrieri F, Cavaliere ML, Wischmeijer A, Mammi C, Neri G, Pisanti MA, Rodella G, Lagana C, Priolo M. 2015. NFIX mutations affecting the DNA-binding domain cause a peculiar overgrowth syndrome (Malan syndrome): a new patients series. Eur J Med Genet 58(9):488–491. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

