This is a preprint.
GSK3 inhibition reduces ECM production and prevents age-related macular degeneration-like pathology
- PMID: 38168310
- PMCID: PMC10760106
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.12.14.571757
GSK3 inhibition reduces ECM production and prevents age-related macular degeneration-like pathology
Update in
-
GSK3 inhibition reduces ECM production and prevents age-related macular degeneration-like pathology.JCI Insight. 2024 Aug 8;9(15):e178050. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.178050. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 39114980 Free PMC article.
Abstract
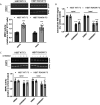
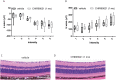
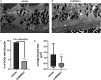
Malattia Leventinese/Doyne Honeycomb Retinal Dystrophy (ML/DHRD) is an age-related macular degeneration (AMD)-like retinal dystrophy caused by an autosomal dominant R345W mutation in the secreted glycoprotein, fibulin-3 (F3). To identify new small molecules that reduce F3 production from retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) cells, we knocked-in a luminescent peptide tag (HiBiT) into the endogenous F3 locus which enabled simple, sensitive, and high throughput detection of the protein. The GSK3 inhibitor, CHIR99021 (CHIR), significantly reduced F3 burden (expression, secretion, and intracellular levels) in immortalized RPE and non-RPE cells. Low-level, long-term CHIR treatment promoted remodeling of the RPE extracellular matrix (ECM), reducing sub-RPE deposit-associated proteins (e.g., amelotin, complement component 3, collagen IV, and fibronectin), while increasing RPE differentiation factors (e.g., tyrosinase, and pigment epithelium derived factor). In vivo, treatment of 8 mo R345W+/+ knockin mice with CHIR (25 mg/kg i.p., 1 mo) was well tolerated and significantly reduced R345W F3-associated AMD-like basal laminar deposit number and size, thereby preventing the main pathological feature in these mice. This is the first demonstration of small molecule-based prevention of AMD-like pathology in ML/DHRD mice and may herald a rejuvenation of interest in GSK3 inhibition for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, including, potentially AMD itself.
Keywords: AMD; CHIR99021; DHRD; EFEMP1; F3; ML; fibulin-3; glycogen synthase kinase 3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
Figures

References
-
- Fernandez-Godino R, Pierce EA, and Garland DL. Extracellular Matrix Alterations and Deposit Formation in AMD. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;854:53–8. - PubMed
-
- Moore DJ, and Clover GM. The effect of age on the macromolecular permeability of human Bruch's membrane. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science. 2001;42(12):2970–5. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
