This is a preprint.
The Natural Products Discovery Center: Release of the First 8490 Sequenced Strains for Exploring Actinobacteria Biosynthetic Diversity
- PMID: 38168313
- PMCID: PMC10760148
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.12.14.571759
The Natural Products Discovery Center: Release of the First 8490 Sequenced Strains for Exploring Actinobacteria Biosynthetic Diversity
Abstract
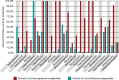
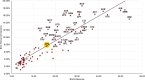
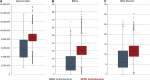
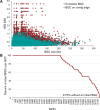
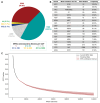
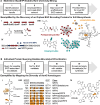
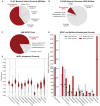
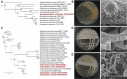
Actinobacteria, the bacterial phylum most renowned for natural product discovery, has been established as a valuable source for drug discovery and biotechnology but is underrepresented within accessible genome and strain collections. Herein, we introduce the Natural Products Discovery Center (NPDC), featuring 122,449 strains assembled over eight decades, the genomes of the first 8490 NPDC strains (7142 Actinobacteria), and the online NPDC Portal making both strains and genomes publicly available. A comparative survey of RefSeq and NPDC Actinobacteria highlights the taxonomic and biosynthetic diversity within the NPDC collection, including three new genera, hundreds of new species, and ~7000 new gene cluster families. Selected examples demonstrate how the NPDC Portal's strain metadata, genomes, and biosynthetic gene clusters can be leveraged using genome mining approaches. Our findings underscore the ongoing significance of Actinobacteria in natural product discovery, and the NPDC serves as an unparalleled resource for both Actinobacteria strains and genomes.
Keywords: Actinobacteria; Biosynthetic gene clusters; Esperamicin; Natural Products Discovery Center; Natural products.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interest Statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Discovery of phosphonic acid natural products by mining the genomes of 10,000 actinomycetes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 29;112(39):12175-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1500873112. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26324907 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing rare marine actinomycete genomes reveals high density of unique natural product biosynthetic gene clusters.Microbiology (Reading). 2016 Dec;162(12):2075-2086. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000386. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Microbiology (Reading). 2016. PMID: 27902408 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of the leinamycin family of natural products by mining actinobacterial genomes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Dec 26;114(52):E11131-E11140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1716245115. Epub 2017 Dec 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 29229819 Free PMC article.
-
In depth natural product discovery - Myxobacterial strains that provided multiple secondary metabolites.Biotechnol Adv. 2020 Mar-Apr;39:107480. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.107480. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Biotechnol Adv. 2020. PMID: 31707075 Review.
-
Micrococcus spp. as a promising source for drug discovery: A review.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Feb 17;50(1):kuad017. doi: 10.1093/jimb/kuad017. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37460166 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Newman D. J. & Cragg G. M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 83, 770–803 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Jones D., Metzger H. J., Schatz A. & Control S.A. W. of gram-negative bacteria in experimental animals by streptomycin. Science 100, 103–105 (1944). - PubMed
-
- Katz L. & Baltz R. H. Natural product discovery: past, present, and future. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 43, 155–176 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
