High-dose benzodiazepine use and QTc interval prolongation, a latent class analysis study
- PMID: 38168538
- PMCID: PMC10762262
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-50489-3
High-dose benzodiazepine use and QTc interval prolongation, a latent class analysis study
Abstract
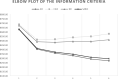
Benzodiazepine (BDZ) addiction is a widespread and multifaceted phenomenon. For many patients, especially females, the concomitant use of other drugs also increases their risk of QTc prolongation, possibly leading to complications such as seizures and even sudden death. However, the relationship between BDZ use and QTc prolongation is currently unclear. The present study aims to examine patterns of polysubstance use among a sample of Italian adults with BDZ dependence in relation with their QTc prolongation risk. We used Latent Class Analysis (LCA) on data collected from 251 inpatients of the Addiction Medicine Unit in Verona to group patients into three classes according to their substance use and their QTc prolongation risk. Results showed no significant relationship between QTc prolongation and BDZ use in any of the classes considered. We conclude that BDZs, even if used long-term and at high dosages, can be considered safe in terms of cardiovascular complications for patients.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials