The N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Antagonist Dextromethorphan Improves Glucose Homeostasis and Preserves Pancreatic Islets in NOD Mice
- PMID: 38168730
- PMCID: PMC10901624
- DOI: 10.1055/a-2236-8625
The N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Antagonist Dextromethorphan Improves Glucose Homeostasis and Preserves Pancreatic Islets in NOD Mice
Abstract
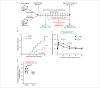
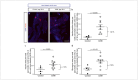
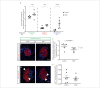
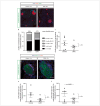
For treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus, a combination of immune-based interventions and medication to promote beta-cell survival and proliferation has been proposed. Dextromethorphan (DXM) is an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist with a good safety profile, and to date, preclinical and clinical evidence for blood glucose-lowering and islet-cell-protective effects of DXM have only been provided for animals and individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Here, we assessed the potential anti-diabetic effects of DXM in the non-obese diabetic mouse model of type 1 diabetes. More specifically, we showed that DXM treatment led to five-fold higher numbers of pancreatic islets and more than two-fold larger alpha- and beta-cell areas compared to untreated mice. Further, DXM treatment improved glucose homeostasis and reduced diabetes incidence by 50%. Our data highlight DXM as a novel candidate for adjunct treatment of preclinical or recent-onset type 1 diabetes.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial-License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
A.W., T.M., E.M. and E.L. declare the following competing financial interests: these authors are inventors of the US patent 10,464,904 entitled “Dextrorphan-derivatives with suppressed central nervous activity”; and T.M. and E.L. are inventors of the US patent 9,370,511 entitled “Morphinan-derivatives for treating diabetes and related disorders.”
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peripherally active dextromethorphan derivatives lower blood glucose levels by targeting pancreatic islets.Cell Chem Biol. 2021 Oct 21;28(10):1474-1488.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2021.05.011. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Cell Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 34118188
-
Need for Better Diabetes Treatment: The Therapeutic Potential of NMDA Receptor Antagonists.Klin Padiatr. 2017 Jan;229(1):14-20. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-117831. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Klin Padiatr. 2017. PMID: 27975343 Review. English.
-
Characterization of pancreatic NMDA receptors as possible drug targets for diabetes treatment.Nat Med. 2015 Apr;21(4):363-72. doi: 10.1038/nm.3822. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 25774850
-
Protection of pancreatic islets from oxidative cell death by a peripherally-active morphinan with increased drug safety.Mol Metab. 2023 Sep;75:101775. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101775. Epub 2023 Jul 12. Mol Metab. 2023. PMID: 37451343 Free PMC article.
-
NMDAR antagonists for the treatment of diabetes mellitus-Current status and future directions.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017 Sep;19 Suppl 1:95-106. doi: 10.1111/dom.13017. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017. PMID: 28880473 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of NMDA Receptor Inhibition by Biguanide Compounds.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 19;17(9):1234. doi: 10.3390/ph17091234. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338396 Free PMC article.
-
The role of GABA in type 1 diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 15;15:1453396. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1453396. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39619323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disease-modifying pharmacological treatments of type 1 diabetes: Molecular mechanisms, target checkpoints, and possible combinatorial treatments.Pharmacol Rev. 2025 Mar;77(2):100044. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmr.2025.100044. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Pharmacol Rev. 2025. PMID: 40014914 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beck R W, Bergenstal R M, Laffel L M et al.Advances in technology for management of type 1 diabetes. Lancet. 2019;394:1265–1273. - PubMed
-
- Kramer C K, Retnakaran R, Zinman B. Insulin and insulin analogs as antidiabetic therapy: A perspective from clinical trials. Cell Metab. 2021;33:740–747. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

