Identify gestational diabetes mellitus by deep learning model from cell-free DNA at the early gestation stage
- PMID: 38168840
- PMCID: PMC10782912
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbad492
Identify gestational diabetes mellitus by deep learning model from cell-free DNA at the early gestation stage
Abstract
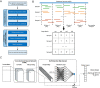
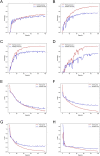
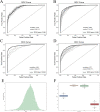
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a common complication of pregnancy, which has significant adverse effects on both the mother and fetus. The incidence of GDM is increasing globally, and early diagnosis is critical for timely treatment and reducing the risk of poor pregnancy outcomes. GDM is usually diagnosed and detected after 24 weeks of gestation, while complications due to GDM can occur much earlier. Copy number variations (CNVs) can be a possible biomarker for GDM diagnosis and screening in the early gestation stage. In this study, we proposed a machine-learning method to screen GDM in the early stage of gestation using cell-free DNA (cfDNA) sequencing data from maternal plasma. Five thousand and eighty-five patients from north regions of Mainland China, including 1942 GDM, were recruited. A non-overlapping sliding window method was applied for CNV coverage screening on low-coverage (~0.2×) sequencing data. The CNV coverage was fed to a convolutional neural network with attention architecture for the binary classification. The model achieved a classification accuracy of 88.14%, precision of 84.07%, recall of 93.04%, F1-score of 88.33% and AUC of 96.49%. The model identified 2190 genes associated with GDM, including DEFA1, DEFA3 and DEFB1. The enriched gene ontology (GO) terms and KEGG pathways showed that many identified genes are associated with diabetes-related pathways. Our study demonstrates the feasibility of using cfDNA sequencing data and machine-learning methods for early diagnosis of GDM, which may aid in early intervention and prevention of adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Keywords: cell-free DNA; copy number variations; deep learning; gestational diabetes mellitus.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Longitudinal integrative cell-free DNA analysis in gestational diabetes mellitus.Cell Rep Med. 2024 Aug 20;5(8):101660. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101660. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 39059385 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting gestational diabetes mellitus risk at 11-13 weeks' gestation: the role of extrachromosomal circular DNA.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Aug 7;23(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02381-1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39113025 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of risk factors and pregnancy outcomes of gestational diabetes mellitus diagnosed during early and late pregnancy.Midwifery. 2018 Nov;66:64-69. doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2018.07.017. Epub 2018 Aug 2. Midwifery. 2018. PMID: 30130677
-
Screening and diagnosing gestational diabetes mellitus.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2012 Oct;(210):1-327. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2012. PMID: 24423035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Gestational diabetes mellitus (Update 2019)].Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2019 May;131(Suppl 1):91-102. doi: 10.1007/s00508-018-1419-8. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2019. PMID: 30980150 Review. German.
Cited by
-
The molecular characteristics of DNA damage and repair related to P53 mutation for predicting the recurrence and immunotherapy response in hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 29;15(1):14939. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99853-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40301641 Free PMC article.
-
Validating Multicenter Cohort Circular RNA Model for Early Screening and Diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Diabetes Metab J. 2025 May;49(3):462-474. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0205. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Diabetes Metab J. 2025. PMID: 39978792 Free PMC article.
-
Factors influencing dietary compliance among patients with gestational diabetes mellitus: a retrospective analysis.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Mar 15;17(3):1925-1937. doi: 10.62347/AQVC5045. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40226005 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic architecture and risk prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus in Chinese pregnancies.Nat Commun. 2025 May 5;16(1):4178. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59442-6. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40325049 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal integrative cell-free DNA analysis in gestational diabetes mellitus.Cell Rep Med. 2024 Aug 20;5(8):101660. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101660. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 39059385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McIntyre HD, Catalano P, Zhang C, et al. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2019;5(1):47. - PubMed
-
- Monteiro LJ, Norman JE, Rice GE, Illanes SE. Fetal programming and gestational diabetes mellitus. Placenta 2016;48:S54–60. - PubMed
-
- Pinney SE, Simmons RA. Metabolic programming, epigenetics, and gestational diabetes mellitus. Curr Diab Rep 2012;12:67–74. - PubMed
-
- Hod M, Kapur A, Sacks DA, et al. The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) initiative on gestational diabetes mellitus: a pragmatic guide for diagnosis, management, and care. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2015;131:S173–211. - PubMed

