Non-mutational neoantigens in disease
- PMID: 38168954
- PMCID: PMC11075006
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-023-01664-1
Non-mutational neoantigens in disease
Abstract
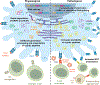
The ability of mammals to mount adaptive immune responses culminating with the establishment of immunological memory is predicated on the ability of the mature T cell repertoire to recognize antigenic peptides presented by syngeneic MHC class I and II molecules. Although it is widely believed that mature T cells are highly skewed towards the recognition of antigenic peptides originating from genetically diverse (for example, foreign or mutated) protein-coding regions, preclinical and clinical data rather demonstrate that novel antigenic determinants efficiently recognized by mature T cells can emerge from a variety of non-mutational mechanisms. In this Review, we describe various mechanisms that underlie the formation of bona fide non-mutational neoantigens, such as epitope mimicry, upregulation of cryptic epitopes, usage of non-canonical initiation codons, alternative RNA splicing, and defective ribosomal RNA processing, as well as both enzymatic and non-enzymatic post-translational protein modifications. Moreover, we discuss the implications of the immune recognition of non-mutational neoantigens for human disease.
© 2024. Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AR081493/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI170897/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI153828/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI143976/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI146180/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI137198/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI127869/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI169723/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AT011419/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG067581/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA274291/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR080593/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA271915/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI134696/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG031782/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

