Inferring super-resolution tissue architecture by integrating spatial transcriptomics with histology
- PMID: 38168986
- PMCID: PMC11260191
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-023-02019-9
Inferring super-resolution tissue architecture by integrating spatial transcriptomics with histology
Abstract
Spatial transcriptomics (ST) has demonstrated enormous potential for generating intricate molecular maps of cells within tissues. Here we present iStar, a method based on hierarchical image feature extraction that integrates ST data and high-resolution histology images to predict spatial gene expression with super-resolution. Our method enhances gene expression resolution to near-single-cell levels in ST and enables gene expression prediction in tissue sections where only histology images are available.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Figures

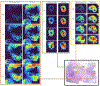


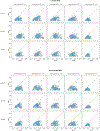
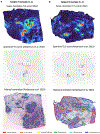
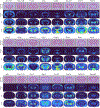





References
-
- Burgess DJ Spatial transcriptomics coming of age. Nat. Rev. Genet 20, 317 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Asp M, Bergenstrahle J. & Lundeberg J. Spatially Resolved Transcriptomes-Next Generation Tools for Tissue Exploration. Bioessays 42, e1900221 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Crosetto N, Bienko M. & van Oudenaarden A. Spatially resolved transcriptomics and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet 16, 57–66 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Moor AE & Itzkovitz S. Spatial transcriptomics: paving the way for tissue-level systems biology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 46, 126–133 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Hu J. et al. SpaGCN: Integrating gene expression, spatial location and histology to identify spatial domains and spatially variable genes by graph convolutional network. Nat. Methods 18, 1342–1351 (2021). - PubMed
Methods-only References
-
- Steiner A. et al. How to train your vit? data, augmentation, and regularization in vision transformers. Preprint at arXiv, 10.48550/arXiv.2106.10270 (2021). - DOI
-
- Xu B, Wang N, Chen T. & Li M. Empirical evaluation of rectified activations in convolutional network. Preprint arXiv, 10.48550/arXiv.1505.00853 (2015). - DOI
-
- Clevert D-A, Unterthiner T. & Hochreiter S. Fast and accurate deep network learning by exponential linear units (ELUs). Preprint at arXiv, 10.48550/arXiv.1511.07289 (2015). - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01EY030192/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- P01AG066597/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- R01GM125301/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01 GM125301/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA266280/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- P30 CA082709/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA264583/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- P01 AG066597/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA266280/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG013185/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001873/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY030192/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HG013158/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)
- R01 HL150359/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL150359/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

