Discovery of sparse, reliable omic biomarkers with Stabl
- PMID: 38168992
- PMCID: PMC11217152
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-023-02033-x
Discovery of sparse, reliable omic biomarkers with Stabl
Abstract
Adoption of high-content omic technologies in clinical studies, coupled with computational methods, has yielded an abundance of candidate biomarkers. However, translating such findings into bona fide clinical biomarkers remains challenging. To facilitate this process, we introduce Stabl, a general machine learning method that identifies a sparse, reliable set of biomarkers by integrating noise injection and a data-driven signal-to-noise threshold into multivariable predictive modeling. Evaluation of Stabl on synthetic datasets and five independent clinical studies demonstrates improved biomarker sparsity and reliability compared to commonly used sparsity-promoting regularization methods while maintaining predictive performance; it distills datasets containing 1,400-35,000 features down to 4-34 candidate biomarkers. Stabl extends to multi-omic integration tasks, enabling biological interpretation of complex predictive models, as it hones in on a shortlist of proteomic, metabolomic and cytometric events predicting labor onset, microbial biomarkers of pre-term birth and a pre-operative immune signature of post-surgical infections. Stabl is available at https://github.com/gregbellan/Stabl .
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.H., B.G., D.K.G. and F.V. are advisory board members; G.B. and X.D. are employed; and E.A.G. is a consultant at SurgeCare. N.A. is a member of the scientific advisory boards of January AI, Parallel Bio, Celine Therapeutics and WellSim Biomedical Technologies, is a paid consultant for MARAbio Systems and is a cofounder of Takeoff AI. Part of this work was carried out while A.M. was on partial leave from Stanford University and was Chief Scientist at nData, Inc. dba, Project N. The present research is unrelated to A.M.’s activity while on leave. J.H., N.A., M.S.A. and B.G. are listed as inventors on a patent application (PCT/US22/71226). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


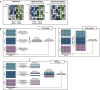
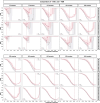
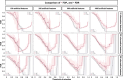

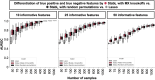


Update of
-
Stabl: sparse and reliable biomarker discovery in predictive modeling of high-dimensional omic data.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 28:rs.3.rs-2609859. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2609859/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Nat Biotechnol. 2024 Oct;42(10):1581-1593. doi: 10.1038/s41587-023-02033-x. PMID: 36909508 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Wafi, A. & Mirnezami, R. Translational -omics: future potential and current challenges in precision medicine. Methods151, 3–11 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Jackson, H. W. et al. The single-cell pathology landscape of breast cancer. Nature578, 615–620 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Dunkler, D., Sánchez-Cabo, F. & Heinze, G. Statistical analysis principles for omics data. Methods Mol. Biol.719, 113–131 (2011). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

