Biophysical characterization of human-cell-expressed, full-length κI O18/O8, AL-09, λ6a, and Wil immunoglobulin light chains
- PMID: 38169170
- PMCID: PMC10939777
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2023.140993
Biophysical characterization of human-cell-expressed, full-length κI O18/O8, AL-09, λ6a, and Wil immunoglobulin light chains
Abstract
Immunoglobulin light chain (AL) amyloidosis involves the deposition of insoluble monoclonal AL protein fibrils in the extracellular space of different organs leading to dysfunction and death. Development of methods to efficiently express and purify AL proteins with acceptable standards of homogeneity and structural integrity has become critical to understand the in vitro and in vivo aspects of AL protein aggregation, and thus the disease progression. In this study, we report the biophysical characterization of His-tagged and untagged versions of AL full-length (FL) κI and λ6 subgroup proteins and their mutants expressed from the Expi293F human cell line. We used an array of biophysical and biochemical methods to analyze the structure and stability of the monomers, oligomerization states, and thermodynamic characteristics of the purified FL proteins and how they compare with the bacterially expressed FL proteins. Our results demonstrate that the tagged and untagged versions of FL proteins have comparable stability to proteins expressed in bacterial cells but exhibit multiple unfolding transitions and reversibility. Non-reducing SDS-PAGE and analytical ultracentrifugation analysis showed presence of monomers and dimers, with an insignificant amount of higher-order oligomers, in the purified fraction of all proteins. Overall, the FL proteins were expressed with sufficient yields for biophysical studies and can replace bacterial expression systems.
Keywords: AL amyloidosis; AL full-length proteins; Circular dichroism; Fluorescence; Mammalian cell protein expression.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest All authors have read and approve of this manuscript and further affirm that the information presented is true and correct and are willing to take public responsibility for the manuscript. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest with the contents of the article.
Figures
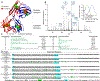






References
-
- Palladini G, Hegenbart U, Milani P, Kimmich C, Foli A, Ho AD, Vidus Rosin M, Albertini R, Moratti R, Merlini G, Schonland S, A staging system for renal outcome and early markers of renal response to chemotherapy in AL amyloidosis, Blood, 124 (2014) 2325–2332. - PubMed
-
- Merlini G, Comenzo RL, Seldin DC, Wechalekar A, Gertz MA, Immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis, Expert Rev Hematol, 7 (2014) 143–156. - PubMed
-
- Glenner GG, Cuatrecasas P, Isersky C, Bladen HA, Eanes ED, Physical and chemical properties of amyloid fibers. II. Isolation of a unique protein constituting the major component from human splenic amyloid fibril concentrates, J Histochem Cytochem, 17 (1969) 769–780. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

