The histidine kinase NahK regulates pyocyanin production through the PQS system
- PMID: 38169296
- PMCID: PMC10809955
- DOI: 10.1128/jb.00276-23
The histidine kinase NahK regulates pyocyanin production through the PQS system
Abstract
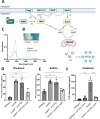
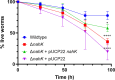
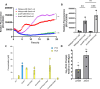
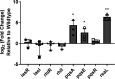
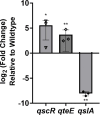
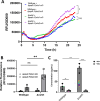
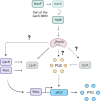
Many bacterial histidine kinases work in two-component systems that combine into larger multi-kinase networks. NahK is one of the kinases in the GacS Multi-Kinase Network (MKN), which is the MKN that controls biofilm regulation in the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This network has also been associated with regulating many virulence factors P. aeruginosa secretes to cause disease. However, the individual role of each kinase is unknown. In this study, we identify NahK as a novel regulator of the phenazine pyocyanin (PYO). Deletion of nahK leads to a fourfold increase in PYO production, almost exclusively through upregulation of phenazine operon two (phz2). We determined that this upregulation is due to mis-regulation of all P. aeruginosa quorum-sensing (QS) systems, with a large upregulation of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal system and a decrease in production of the acyl-homoserine lactone-producing system, las. In addition, we see differences in expression of quorum-sensing inhibitor proteins that align with these changes. Together, these data contribute to understanding how the GacS MKN modulates QS and virulence and suggest a mechanism for cell density-independent regulation of quorum sensing. IMPORTANCE Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram-negative bacterium that establishes biofilms as part of its pathogenicity. P. aeruginosa infections are associated with nosocomial infections. As the prevalence of multi-drug-resistant P. aeruginosa increases, it is essential to understand underlying virulence molecular mechanisms. Histidine kinase NahK is one of several kinases in P. aeruginosa implicated in biofilm formation and dispersal. Previous work has shown that the nitric oxide sensor, NosP, triggers biofilm dispersal by inhibiting NahK. The data presented here demonstrate that NahK plays additional important roles in the P. aeruginosa lifestyle, including regulating bacterial communication mechanisms such as quorum sensing. These effects have larger implications in infection as they affect toxin production and virulence.
Keywords: NahK; NosP; PQS; nitric oxide; pyocyanin; quorum sensing; signaling; virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The histidine kinase NahK regulates denitrification and nitric oxide accumulation through RsmA in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.J Bacteriol. 2025 Jan 31;207(1):e0040824. doi: 10.1128/jb.00408-24. Epub 2024 Dec 11. J Bacteriol. 2025. PMID: 39660891 Free PMC article.
-
The Small RNA AmiL Regulates Quorum Sensing-Mediated Virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Apr 27;10(2):e0221121. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02211-21. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35262393 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Regulation of the Phenazine Biosynthetic Operons by Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1-N.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Jul 23;8:252. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00252. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30083519 Free PMC article.
-
A biomedical perspective of pyocyanin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: its applications and challenges.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Feb 10;40(3):90. doi: 10.1007/s11274-024-03889-0. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38341389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The third quorum-sensing system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Pseudomonas quinolone signal and the enigmatic PqsE protein.J Med Microbiol. 2020 Jan;69(1):25-34. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001116. J Med Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31794380 Review.
Cited by
-
Negative regulation of biofilm formation by nitric oxide sensing proteins.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Aug 31;51(4):1447-1458. doi: 10.1042/BST20220845. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 37610010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The histidine kinase NahK regulates denitrification and nitric oxide accumulation through RsmA in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.J Bacteriol. 2025 Jan 31;207(1):e0040824. doi: 10.1128/jb.00408-24. Epub 2024 Dec 11. J Bacteriol. 2025. PMID: 39660891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Qin S, Xiao W, Zhou C, Pu Q, Deng X, Lan L, Liang H, Song X, Wu M. 2022. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: pathogenesis, virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, interaction with host, technology advances and emerging therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7:199. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01056-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maes M, Higginson E, Pereira-Dias J, Curran MD, Parmar S, Khokhar F, Cuchet-Lourenço D, Lux J, Sharma-Hajela S, Ravenhill B, Hamed I, Heales L, Mahroof R, Soderholm A, Forrest S, Sridhar S, Brown NM, Baker S, Navapurkar V, Dougan G, Scott JB, Morris AC. 2021. Correction to: ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Crit Care 25:130. doi:10.1186/s13054-021-03560-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

