Intravenous iron versus blood transfusion for postpartum anemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38169415
- PMCID: PMC10759729
- DOI: 10.1186/s13643-023-02400-4
Intravenous iron versus blood transfusion for postpartum anemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Intravenous iron (IV-iron) is used as an alternative to, or alongside, red blood cell transfusion (RBC-T) to treat more severe postpartum anemia (PPA), although optimal treatment options remain unclear. No previous systematic reviews have examined IV-iron and RBC-T, including patient-reported outcomes and hematological responses.
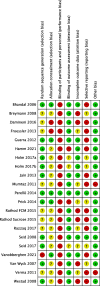
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials comparing IV-iron and RBC-T with each other, oral iron, no treatment, and placebo for the treatment of PPA. Key inclusion criteria were PPA (hemoglobin < 12 g/dL) and IV-iron or RBC-T as interventions. Key exclusion criteria were antenatal IV-iron or RBC-T. Fatigue was the primary outcome. Secondary outcomes included hemoglobin and ferritin concentrations, and adverse events. From 27th August 2020 to 26th September 2022, databases, registries, and hand searches identified studies. A fixed-effect meta-analysis was undertaken using RevMan (5.4) software. The quality of the studies and the evidence was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias table, and Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation. This review is registered with the Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (CRD42020201115).
Results: Twenty studies and 4196 participants were included: 1834 assigned IV-iron, 1771 assigned oral iron, 330 assigned RBC-T, and 261 assigned non-intervention. Six studies reported the primary outcome of fatigue (1251 participants). Only studies of IV-iron vs. oral iron (15 studies) were available for meta-analysis. Of these, three reported on fatigue using different scales; two were available for meta-analysis. There was a significant reduction in fatigue with IV-iron compared to oral iron (standardized mean difference - 0.40, 95% confidence interval (CI) - 0.62, - 0.18, I2 = 0%). The direction of effect also favored IV-iron for hemoglobin (mean difference (MD) 0.54 g/dL, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.47, 0.61, I2 = 91%), ferritin, (MD 58.07 mcg/L, 95% CI 55.74, 60.41, I2 = 99%), and total adverse events (risk-ratio 0.63, 95% CI 0.52, 0.77, I2 = 84%). The overall quality of the evidence was low-moderate.
Discussion: For all outcomes, the evidence for RBC-T, compared to IV-iron, non-intervention, or dose effects of RBC-T is very limited. Further research is needed to determine whether RBC-T or IV-iron for the treatment of PPA is superior for fatigue and hematological outcomes.
Keywords: Adverse drug reaction; Anemia; Erythrocyte transfusion; Fatigue; Ferric compounds; Hematinics; Intravenous infusion; Iron; Iron deficiency; Puerperal disorders.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The fatigue after infusion or transfusion pilot trial and feasibility study: A three-armed randomized pilot trial of intravenous iron and blood transfusion for the treatment of postpartum anemia.Transfusion. 2024 Feb;64(2):301-314. doi: 10.1111/trf.17621. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Transfusion. 2024. PMID: 38149691 Clinical Trial.
-
Oral vs intravenous iron therapy for postpartum anemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Jul;221(1):19-29.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2018.12.016. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019. PMID: 30578747 Free PMC article.
-
Role of preoperative intravenous iron therapy to correct anemia before major surgery: study protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Syst Rev. 2015 Mar 15;4:29. doi: 10.1186/s13643-015-0016-4. Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25874460 Free PMC article.
-
Parenteral versus oral iron therapy for adults and children with chronic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Feb 21;2(2):CD007857. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007857.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30790278 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Postoperative Iron Therapy in Improving Clinical and Patient-Centered Outcomes Following Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Transfus Med Rev. 2018 Apr;32(2):89-101. doi: 10.1016/j.tmrv.2017.10.002. Epub 2017 Oct 22. Transfus Med Rev. 2018. PMID: 29126577
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

