The Therapeutic Efficacy of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Acute Toxoplasmosis in BALB/c Mice
- PMID: 38169550
- PMCID: PMC10758080
- DOI: 10.18502/ijpa.v18i4.14259
The Therapeutic Efficacy of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Acute Toxoplasmosis in BALB/c Mice
Abstract
Background: Toxoplasma gondii infects nearly one-third of the world's population. Due to the significant side effects of current treatment options, identifying safe and effective therapies seems crucial. Nanoparticles (NPs) are new promising compounds in treating pathogenic organisms. Currently, no research has investigated the effects of zinc oxide NPs (ZnO-NPs) on Toxoplasma parasite. We aimed to investigate the therapeutic efficacy of ZnO-NPs against tachyzoite forms of T. gondii, RH strain in BALB/c mice.
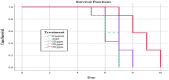
Methods: In an experiment with 35 female BALB/c mice infected with T. gondii tachyzoites, colloidal ZnO-NPs at concentrations of 10, 20, and 50 ppm, as well as a 50 ppm ZnO solution and a control group, were orally administered four hours after inoculation and continued daily until the mices' death. Survival rates were calculated and tachyzoite counts were evaluated in the peritoneal fluids of infected mice.
Results: The administration of ZnO-NPs resulted in the reduction of tachyzoite counts in infected mice compared to both the ZnO-treated and control group (P<0.001). Intervention with ZnO-NPs significantly increased the survival time compared to the control group (6.2±0.28 days, P-value <0.05), additionally, the highest dose of ZnO-NPs (50 ppm) showed the highest mice survival time (8.7±0.42 days).
Conclusion: ZnO-NPs were effective in decreasing the number of tachyzoites and increasing mice survival time in vivo. Moreover, there were no significant differences in survival time between the untreated control group and the group treated with zinc oxide, suggesting that, bulk ZnO is not significantly effective in comparison with ZnONPs.
Keywords: BALB/c mice; Tachyzoite; Toxoplasma gondii; Zinc oxide nanoparticles.
© 2023 Rafei Siahkal et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Zinc oxide nanoparticles produced by Zingiber officinale ameliorates acute toxoplasmosis-induced pathological and biochemical alterations and reduced parasite burden in mice model.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023 Jul 6;17(7):e0011447. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011447. eCollection 2023 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023. PMID: 37410712 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Toxoplasma activity of various molecular weights and concentrations of chitosan nanoparticles on tachyzoites of RH strain.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Mar 8;13:1341-1351. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S158736. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29563791 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, characterization, and antiparasitic effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles-eugenol nanosuspension against Toxoplasma gondii infection.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 19;9(8):e19295. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19295. eCollection 2023 Aug. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37654466 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc Oxide and Magnesium-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Ameliorate Murine Chronic Toxoplasmosis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 15;17(1):113. doi: 10.3390/ph17010113. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256946 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of alginate nanoparticles on the immunogenicity of excretory-secretory antigens against acute toxoplasmosis in murine model.Acta Trop. 2022 Jan;225:106215. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2021.106215. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Acta Trop. 2022. PMID: 34687647
References
-
- Molan A, Nosaka K, Hunter M, Wang W. Global status of Toxoplasma gondii infection: systematic review and prevalence snapshots. Trop Biomed. 2019; 36(4):898–925. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources