Quaternization drives spleen-to-lung tropism conversion for mRNA-loaded lipid-like nanoassemblies
- PMID: 38169552
- PMCID: PMC10758058
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.90071
Quaternization drives spleen-to-lung tropism conversion for mRNA-loaded lipid-like nanoassemblies
Abstract
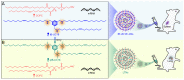
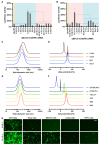
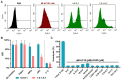
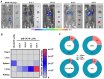
Background: As the overwhelming majority of advanced mRNA delivery systems are preferentially accumulated in the liver, there is an accelerating growth in the demand for the development of non-liver mRNA delivery platforms. Methods: In this study, we prepared cationic lipid-like nanoassemblies through a N-quaternizing strategy. Their physicochemical properties, in vitro mRNA delivery efficiency, and organ tropism in mice were investigated. Results: Introduction of quaternary ammonium groups onto lipid-like nanoassemblies not only enhances their mRNA delivery performance in vitro, but also completely alters their tropism from the spleen to the lung after intravenous administration in mice. Quaternized lipid-like nanoassemblies exhibit ultra-high specificity to the lung and are predominantly taken up by pulmonary immune cells, leading to over 95% of exogenous mRNA translation in the lungs. Such mRNA delivery carriers are stable even after more than one-year storage at ambient temperature. Conclusions: Quaternization provides an alternative method for design of new lung-targeted mRNA delivery systems without incorporation of targeting ligands, which should extend the therapeutic applicability of mRNA to lung diseases.
Keywords: lipid-like nanoassembly; lung targeting; quaternization; systemic mRNA delivery; ultra-high selectivity.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors declare the following financial interest which may be considered as potential competing interests: Y. Huang, J. Wu, S. Li, and B. Li are listed as inventors on an issued patent related to this work.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

