ALKBH1 rs2267755 C>T polymorphism decreases neuroblastoma risk in Chinese children
- PMID: 38169562
- PMCID: PMC10758041
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.89271
ALKBH1 rs2267755 C>T polymorphism decreases neuroblastoma risk in Chinese children
Abstract
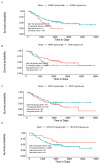
Neuroblastoma is a highly malignant extracranial solid tumor in pediatrics. ALKBH1 as a recently discovered DNA N6-methyldeoxyadenosine (6mA) demethylase closely links to tumorigenesis. Whether the ALKBH1 polymorphism contributes to neuroblastoma risk remains unclear. In the present study, we genotyped the ALKBH1 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 402 neuroblastoma patients and 473 healthy controls by TaqMan assay. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were also calculated to evaluate the strength of the association. Our result exhibited that the rs2267755 C>T (CT vs. CC, adjusted OR=0.69, 95% CI=0.50-0.94, P=0.019) is significantly associated with reduced neuroblastoma risk. And its protective effect is particularly significant in children with tumors originating from the retroperitoneal. Combined genotype analysis revealed that carriers with 1-2 protective genotypes are more susceptible to neuroblastoma than those with 3-4 protective genotypes (adjusted OR=0.71, 95% CI=0.53-0.97, P=0.028). Moreover, the rs2267755 C>T is significantly associated with messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of ALKBH1 and three of its surrounding genes, including SNWQ, ADCK1, and RPL21P10. These results suggest that the rs2267755 C>T may be a genetic variant to reduce neuroblastoma risk.
Keywords: ALKBH1; neuroblastoma; polymorphism; susceptibility.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ALKBH5 gene polymorphisms and risk of neuroblastoma in Chinese children from Jiangsu Province.Cancer Innov. 2023 Dec 22;3(2):e103. doi: 10.1002/cai2.103. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cancer Innov. 2023. PMID: 38946930 Free PMC article.
-
Potentially functional polymorphisms in the LIN28B gene contribute to neuroblastoma susceptibility in Chinese children.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Aug;20(8):1534-41. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12846. Epub 2016 Mar 29. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27021521 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between WTAP gene polymorphisms and neuroblastoma susceptibility in Chinese children.Transl Pediatr. 2021 Jan;10(1):146-152. doi: 10.21037/tp-20-168. Transl Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33633946 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the LINC00673 rs11655237 C> T polymorphisms with cancer risk in the Chinese population: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Sep 16;101(37):e30353. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030353. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36123911 Free PMC article.
-
The biological function of demethylase ALKBH1 and its role in human diseases.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 24;10(13):e33489. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33489. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39040364 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polymorphisms in the NSUN1 gene and neuroblastoma risk in Chinese children from Jiangsu province.J Cancer. 2025 Jan 1;16(2):622-628. doi: 10.7150/jca.103097. eCollection 2025. J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39744478 Free PMC article.
-
Research status and development trends of omics in neuroblastoma a bibliometric and visualization analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 10;14:1383805. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1383805. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39450262 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of NEFL gene polymorphisms with neuroblastoma risk in Chinese children from Jiangsu Province.Transl Pediatr. 2025 May 30;14(5):984-991. doi: 10.21037/tp-2024-611. Epub 2025 May 26. Transl Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40519736 Free PMC article.
-
Dealkylation of Macromolecules by Eukaryotic α-Ketoglutarate-Dependent Dioxygenases from the AlkB-like Family.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Sep 20;46(9):10462-10491. doi: 10.3390/cimb46090622. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39329974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ishola TA, Chung DH. Neuroblastoma. Surg Oncol. 2007;16:149–56. - PubMed
-
- Durinck K, Speleman F. Epigenetic regulation of neuroblastoma development. Cell Tissue Res. 2018;372:309–24. - PubMed
-
- Bartolucci S, Estenoz M, Longo A, Santoro B, Momparler RL, Rossi M. et al. 5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine as inducer of differentiation and growth inhibition in mouse neuroblastoma cells. Cell Differ Dev. 1989;27:47–55. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

