SGK3 promotes vascular calcification via Pit-1 in chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 38169564
- PMCID: PMC10758069
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.87317
SGK3 promotes vascular calcification via Pit-1 in chronic kidney disease
Abstract
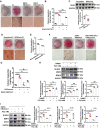
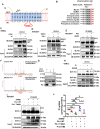
Rationale: Vascular calcification (VC) is a life-threatening complication in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) caused mainly by hyperphosphatemia. However, the regulation of VC remains unclear despite extensive research. Although serum- and glucocorticoid-induced kinase 3 (SGK3) regulate the sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporters in the intestine and kidney, its effect on VC in CKD remains unknown. Additionally, type III sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporter-1 (Pit-1) plays a significant role in VC development induced by high phosphate in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). However, it remains unclear whether SGK3 regulates Pit-1 and how exactly SGK3 promotes VC in CKD via Pit-1 at the molecular level. Thus, we investigated the role of SGK3 in the certified outflow vein of arteriovenous fistulas (AVF) and aortas of uremic mice. Methods and Results: In our study, using uremic mice, we observed a significant upregulation of SGK3 and calcium deposition in certified outflow veins of the AVF and aortas, and the increase expression of SGK3 was positively correlated with calcium deposition in uremic aortas. In vitro, the downregulation of SGK3 reversed VSMCs calcification and phenotype switching induced by high phosphate. Mechanistically, SGK3 activation enhanced the mRNA transcription of Pit-1 through NF-κB, downregulated the ubiquitin-proteasome mediated degradation of Pit-1 via inhibiting the activity of neural precursor cells expressing developmentally downregulated protein 4 subtype 2 (Nedd4-2), an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Moreover, under high phosphate stimulation, the enhanced phosphate uptake induced by SGK3 activation was independent of the increased protein expression of Pit-1. Our co-immunoprecipitation and in vitro kinase assays confirmed that SGK3 interacts with Pit-1 through Thr468 in loop7, leading to enhanced phosphate uptake. Conclusion: Thus, it is justifiable to conclude that SGK3 promotes VC in CKD by enhancing the expression and activities of Pit-1, which indicate that SGK3 could be a therapeutic target for VC in CKD.
Keywords: Pit-1; SGK3; chronic kidney disease; ubiquitin-proteasome pathway; vascular calcification.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





References
-
- Daniel WT, Weber C, Bailey JA, Raggi P, Sharma J. Prospective analysis of coronary calcium in patients on dialysis undergoing a near-total parathyroidectomy. Surgery. 2013;154(6):p.. 1315-21; discussion 1321-2. - PubMed
-
- Dong K, He X, Hu G, Yao Y, Zhou J. Coronary artery disease risk gene PRDM16 is preferentially expressed in vascular smooth muscle cells and a potential novel regulator of smooth muscle homeostasis. bioRxiv. 2023. 2023. 04. 03.535461.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

