Combined BET and MEK Inhibition synergistically suppresses melanoma by targeting YAP1
- PMID: 38169595
- PMCID: PMC10758063
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.85437
Combined BET and MEK Inhibition synergistically suppresses melanoma by targeting YAP1
Abstract
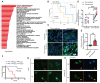
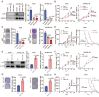
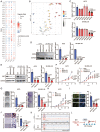
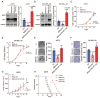
Rationale: The response rate to the MEK inhibitor trametinib in BRAF-mutated melanoma patients is less than 30%, and drug resistance develops rapidly, but the mechanism is still unclear. Yes1-associated transcriptional regulator (YAP1) is highly expressed in melanoma and may be related to MEK inhibitor resistance. The purpose of this study was to investigate the mechanism of YAP1 in MEK inhibitor resistance in melanoma and to screen YAP1 inhibitors to further determine whether YAP1 inhibition reverses MEK inhibitor resistance. Methods: On the one hand, we analyzed paired melanoma and adjacent tissue samples using RNA-seq and found that the Hippo-YAP1 signaling pathway was the top upregulated pathway. On the other hand, we evaluated the transcriptomes of melanoma samples from patients before and after trametinib treatment and investigated the correlation between YAP1 expression and trametinib resistance. Then, we screened for inhibitors that repress YAP1 expression and investigated the mechanisms. Finally, we investigated the antitumor effect of YAP1 inhibition combined with MEK inhibition both in vitro and in vivo. Results: We found that YAP1 expression levels upon trametinib treatment in melanoma patients were correlated with resistance to trametinib. YAP1 was translocated into the nucleus after trametinib treatment in melanoma cells, which could render resistance to MEK inhibition. Thus, we screened for inhibitors that repress YAP1 expression and identified multiple bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) inhibitors, including NHWD-870, as hits. BET inhibition repressed YAP1 expression by decreasing BRD4 binding to the YAP1 promoter. Consistently, YAP1 overexpression was sufficient to reverse the proliferation defect caused by BRD4 depletion. In addition, the BET inhibitor NHWD-870 acted synergistically with trametinib to suppress melanoma growth in vitro and in vivo. Conclusions: We identified a new vulnerability for MEK inhibitor-resistant melanomas, which activated Hippo pathway due to elevated YAP1 activity. Inhibition of BRD4 using BET inhibitors suppressed YAP1 expression and led to blunted melanoma growth when combined with treatment with the MEK inhibitor trametinib.
Keywords: BET inhibitor; BRD4; MEK inhibitor; Melanoma; YAP1.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
YAP1 Mediates Resistance to MEK1/2 Inhibition in Neuroblastomas with Hyperactivated RAS Signaling.Cancer Res. 2019 Dec 15;79(24):6204-6214. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-1415. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31672841 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Hippo coactivator YAP1 through BET bromodomain inhibition in esophageal adenocarcinoma.Mol Oncol. 2020 Jun;14(6):1410-1426. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12667. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32175692 Free PMC article.
-
Yap1 Mediates Trametinib Resistance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas.Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Apr 15;27(8):2326-2339. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-4179. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33547198 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Trametinib in metastatic melanoma.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2015;15(7):749-60. doi: 10.1586/14737140.2015.1060127. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 26107021 Review.
-
"RB-reactivator screening" as a novel cell-based assay for discoveries of molecular targeting agents including the first-in-class MEK inhibitor trametinib (trade name: Mekinist).Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Aug;236:108234. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108234. Epub 2022 Jun 19. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35732246 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomimetic Nano-delivery of Small-Molecule Piceatannol Modulates Tumor Stemness and Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Metastasis via Hippo/YAP1/SOX9 Signaling.Small. 2025 Jan;21(2):e2407191. doi: 10.1002/smll.202407191. Epub 2024 Nov 10. Small. 2025. PMID: 39523731 Free PMC article.
-
Opportunities, obstacles and challenges of nano-immunotherapy in melanoma.Front Immunol. 2025 Aug 8;16:1611423. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1611423. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40861441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focus on mechano-immunology: new direction in cancer treatment.Int J Surg. 2025 Mar 1;111(3):2590-2602. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002224. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 39764598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic Lethality between Cohesin and WNT Signaling Pathways in Diverse Cancer Contexts.Cells. 2024 Mar 30;13(7):608. doi: 10.3390/cells13070608. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38607047 Free PMC article.
-
TME-responsive nanocomposite hydrogel with targeted capacity for enhanced synergistic chemoimmunotherapy of MYC-amplified osteosarcoma.Bioact Mater. 2025 Jan 14;47:83-99. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.01.006. eCollection 2025 May. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 39897587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Robert C, Karaszewska B, Schachter J, Rutkowski P, Mackiewicz A, Stroiakovski D. et al. Improved overall survival in melanoma with combined dabrafenib and trametinib. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(1):30–9. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

