METTL3 boosts mitochondrial fission and induces cardiac fibrosis after ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 38169612
- PMCID: PMC10758110
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.87535
METTL3 boosts mitochondrial fission and induces cardiac fibrosis after ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
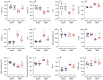
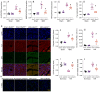
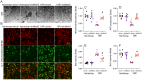
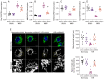
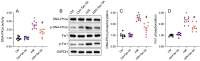
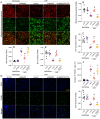
METTL3, an RNA methyltransferase enzyme, exerts therapeutic effects on various cardiovascular diseases. Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MIRI) and subsequently cardiac fibrosis is linked to acute cardiomyocyte death or dysfunction induced by mitochondrial damage, particularly mitochondrial fission. Our research aims to elucidate the potential mechanisms underlying the therapeutic actions of METTL3 in MIRI, with focus on mitochondrial fission. When compared with Mettl3flox mice subjected to MIRI, Mettl3 cardiomyocyte knockout (Mettl3Cko) mice have reduced infarct size, decreased serum levels of myocardial injury-related factors, limited cardiac fibrosis, and preserved myocardial ultrastructure and contractile/relaxation capacity. The cardioprotective actions of Mettl3 knockout were associated with reduced inflammatory responses, decreased myocardial neutrophil infiltration, and suppression of cardiomyocyte death. Through signaling pathway validation experiments and assays in cultured HL-1 cardiomyocytes exposed to hypoxia/reoxygenation, we confirmed that Mettl3 deficiency interfere with DNA-PKcs phosphorylation, thereby blocking the downstream activation of Fis1 and preventing pathological mitochondrial fission. In conclusion, this study confirms that inhibition of METTL3 can alleviate myocardial cardiac fibrosis inflammation and prevent cardiomyocyte death under reperfusion injury conditions by disrupting DNA-PKcs/Fis1-dependent mitochondrial fission, ultimately improving cardiac function. These findings suggest new approaches for clinical intervention in patients with MIRI.
Keywords: DNA-PKcs; Fis1; METTL3; cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury.; mitochondrial fission.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aerobic exercise training attenuates ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by decreasing the methylation level of METTL3-associated m6A RNA in cardiomyocytes.Life Sci. 2025 Jan 15;361:123294. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.123294. Epub 2024 Dec 5. Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39645164
-
lncRNA Oip5-as1 inhibits excessive mitochondrial fission in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by modulating DRP1 phosphorylation.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 May 14;29(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00588-4. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38745296 Free PMC article.
-
METTL3, m6A modification, and EGR1: interplay affecting myocardial I/R injury outcomes.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Dec 21;41(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09937-7. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39707117 Free PMC article.
-
Novel roles of κ-opioid receptor in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.PeerJ. 2024 Jun 25;12:e17333. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17333. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38948204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Oct;123:110714. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110714. Epub 2023 Jul 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37523969 Review.
Cited by
-
BuyangHuanwu Decoction alleviates Endothelial Cell Apoptosis and Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction via Regulation of the MAPKK4/p38 Signaling Axis.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Sep 23;21(13):2464-2479. doi: 10.7150/ijms.98183. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39439466 Free PMC article.
-
m6A Ribonucleic Acid Methylation in Fibrotic Diseases of Visceral Organs.Small Sci. 2024 Nov 21;5(2):2400308. doi: 10.1002/smsc.202400308. eCollection 2025 Feb. Small Sci. 2024. PMID: 40213062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic modifications in cardiac fibrosis: recent evidence of new pharmacological targets.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 May 2;12:1583446. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1583446. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40384946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL3 mediates CPB1 expression by regulating transcription factor BACH2 to promote apoptosis and oxidative stress of lens epithelial cells.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2025 Jun;57(2-3):161-171. doi: 10.1007/s10863-025-10054-1. Epub 2025 Feb 21. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2025. PMID: 39982642
-
Role of M6a Methylation in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024 Sep;24(9):918-928. doi: 10.1007/s12012-024-09898-7. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39026038 Review.
References
-
- Zhu H, Toan S, Mui D, Zhou H. Mitochondrial quality surveillance as a therapeutic target in myocardial infarction. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2021;231:e13590. - PubMed
-
- Zhou H, Ren J, Toan S, Mui D. Role of mitochondrial quality surveillance in myocardial infarction: From bench to bedside. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;66:101250. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

