Radiotherapy in Preclinical Models of Brain Metastases: A Review and Recommendations for Future Studies
- PMID: 38169621
- PMCID: PMC10758094
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.91295
Radiotherapy in Preclinical Models of Brain Metastases: A Review and Recommendations for Future Studies
Abstract
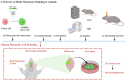
Brain metastases (BMs) frequently occur in primary tumors such as lung cancer, breast cancer, and melanoma, and are associated with notably short natural survival. In addition to surgical interventions, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, radiotherapy (RT) is a crucial treatment for BM and encompasses whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) and stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). Validating the efficacy and safety of treatment regimens through preclinical models is imperative for successful translation to clinical application. This not only advances fundamental research but also forms the theoretical foundation for clinical study. This review, grounded in animal models of brain metastases (AM-BM), explores the theoretical underpinnings and practical applications of radiotherapy in combination with chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and emerging technologies such as nanomaterials and oxygen-containing microbubbles. Initially, we provided a concise overview of the establishment of AM-BMs. Subsequently, we summarize key RT parameters (RT mode, dose, fraction, dose rate) and their corresponding effects in AM-BMs. Finally, we present a comprehensive analysis of the current research status and future directions for combination therapy based on RT. In summary, there is presently no standardized regimen for AM-BM treatment involving RT. Further research is essential to deepen our understanding of the relationships between various parameters and their respective effects.
Keywords: Animal models; Brain metastasis; Combined modality therapy; Dose fractionation, Radiation; Radiotherapy.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Biological implications of whole-brain radiotherapy versus stereotactic radiosurgery of multiple brain metastases.J Neurosurg. 2014 Dec;121 Suppl:60-8. doi: 10.3171/2014.7.GKS141229. J Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 25434938
-
Radiotherapy in combination with systemic therapies for brain metastases: current status and progress.Cancer Biol Med. 2020 Nov 15;17(4):910-922. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0109. Epub 2020 Dec 15. Cancer Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 33299643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cost-effectiveness of stereotactic radiosurgery with and without whole-brain radiotherapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed brain metastases.J Neurosurg. 2014 Dec;121 Suppl:84-90. doi: 10.3171/2014.7.GKS14972. J Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 25434941
-
Prognostic factors for survival in patients treated with stereotactic radiosurgery for recurrent brain metastases after prior whole brain radiotherapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012 May 1;83(1):303-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.06.1987. Epub 2011 Nov 11. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012. PMID: 22079723
-
Congress of Neurological Surgeons Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guidelines on the Role of Whole Brain Radiation Therapy in Adults With Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Brain Tumors.Neurosurgery. 2019 Mar 1;84(3):E159-E162. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyy541. Neurosurgery. 2019. PMID: 30629211
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of online adaptive magnetic resonance-guided fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer (GASTO-1075): a single-arm, phase 2 trial.EClinicalMedicine. 2025 Apr 9;82:103189. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2025.103189. eCollection 2025 Apr. EClinicalMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40247887 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Standardized Training Resident on Pain Management in Patients with Advanced Lung Cancer.J Cancer Educ. 2025 Jun;40(3):388-395. doi: 10.1007/s13187-024-02519-5. Epub 2024 Oct 27. J Cancer Educ. 2025. PMID: 39461905
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing elucidated the landscape of breast cancer brain metastases and identified ILF2 as a potential therapeutic target.Cell Prolif. 2024 Nov;57(11):e13697. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13697. Epub 2024 Jun 29. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 38943472 Free PMC article.
-
Metastatic brain tumors: from development to cutting-edge treatment.MedComm (2020). 2024 Dec 20;6(1):e70020. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70020. eCollection 2025 Jan. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39712454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Refining Lung Cancer Brain Metastasis Models for Spatiotemporal Dynamic Research and Personalized Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2025 May 7;17(9):1588. doi: 10.3390/cancers17091588. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361513 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

