MAPK1 Mediates MAM Disruption and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Diabetic Kidney Disease via the PACS-2-Dependent Mechanism
- PMID: 38169625
- PMCID: PMC10758092
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.89291
MAPK1 Mediates MAM Disruption and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Diabetic Kidney Disease via the PACS-2-Dependent Mechanism
Abstract
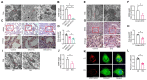
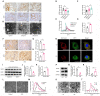
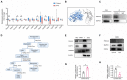
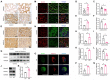
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a leading cause of end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Mitochondrial dysfunction in renal tubules, occurring early in the disease, is linked to the development of DKD, although the underlying pathways remain unclear. Here, we examine diabetic human and mouse kidneys, and HK-2 cells exposed to high glucose, to show that high glucose disrupts mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane (MAM) and causes mitochondrial fragmentation. We find that high glucose conditions increase mitogen-activated protein kinase 1(MAPK1), a member of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway, which in turn lowers the level of phosphofurin acidic cluster sorting protein 2 (PACS-2), a key component of MAM that tethers mitochondria to the ER. MAPK1-induced disruption of MAM leads to mitochondrial fragmentation but this can be rescued in HK-2 cells by increasing PACS-2 levels. Functional studies in diabetic mice show that inhibition of MAPK1 increases PACS-2 and protects against the loss of MAM and the mitochondrial fragmentation. Taken together, these results identify the MAPK1-PACS-2 axis as a key pathway to therapeutically target as well as provide new insights into the pathogenesis of DKD.
Keywords: MAPK1; PACS-2; diabetic kidney disease; mitochondria; mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
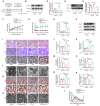
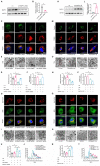
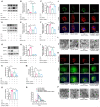
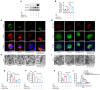
References
-
- Reutens AT. Epidemiology of diabetic kidney disease. Med Clin North Am. 2013;97:1–18. - PubMed
-
- Tuttle KR, Bakris GL, Bilous RW, Chiang JL, de Boer IH, Goldstein-Fuchs J. et al. Diabetic kidney disease: a report from an ADA Consensus Conference. American journal of kidney diseases: the official journal of the National Kidney Foundation. 2014;64:510–33. - PubMed
-
- White SL, Cass A, Atkins RC, Chadban SJ. Chronic kidney disease in the general population. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2005;12:5–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

