The Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance Index is Superior to the Triglyceride and Glucose Index in Identifying Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Hyperuricemia Subjects
- PMID: 38169634
- PMCID: PMC10758352
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S438975
The Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance Index is Superior to the Triglyceride and Glucose Index in Identifying Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Hyperuricemia Subjects
Abstract
Purpose: Hyperuricemia (HUA) is a recognized risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Early diagnosis and the identification of predictive factors are important for the HUA population. This study aimed to investigate the potential relationship between the metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) index and the triglyceride and glucose (TyG) index with NAFLD in individuals with HUA.
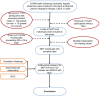
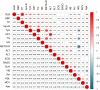
Patients and methods: A total of 5537 HUA participants were included in the study. Hepatic ultrasonography was conducted following the latest diagnostic criteria to diagnose NAFLD. The relationship between the TyG and METS-IR index and NAFLD was evaluated by multivariable logistic regression analysis and restricted cubic spline model (RCS). In addition, the area under the curve (AUC), positive likelihood ratio, and negative likelihood ratio were explored to compare the predictive value of IR surrogates for NAFLD with HUA. The AUCs of the two indicators were compared using the DeLong test.
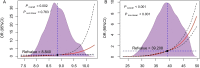
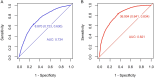
Results: Multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed that elevated TyG (OR = 2.285, 95% CI: 1.525, 3.428) and METS-IR (OR = 1.242, 95% CI: 1.219, 1.266) indices significantly increase the risk of NAFLD. Meanwhile, the RCS analysis revealed a -log-shaped nonlinear relationship between NAFLD risk and the METS-IR index (P non-linear < 0.001), contrasting with the linear association observed with the TyG index (P non-linear = 0.763). Notably, the risk of NAFLD demonstrated a significant escalation when the METS-IR index exceeded the threshold of 39.208 (OR=1). Compared to the TyG index (AUC = 0.734, 95% CI: 0.721~0.748), the METS-IR index (AUC = 0.821, 95% CI: 0.810~0.832) demonstrated superior predictive value for NAFLD in individuals with HUA according to the DeLong test.
Conclusion: In the HUA population, the METS-IR index has a higher predictive value for NAFLD than the TyG index, contributing to early diagnosis and disease prevention.
Keywords: hyperuricemia; inflammation; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; the metabolic score for insulin resistance index; the triglyceride and glucose index.
© 2023 Shu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of the predictive value of TyG index and METS-IR for OSA combined with NAFLD: a retrospective observational study based on a physical examination population.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr 21;25(1):279. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03856-5. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40259241 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride-Glucose Index is Significantly Associated with the Risk of Hyperuricemia in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 May 8;16:1323-1334. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S408075. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 37188227 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship Between Six Insulin Resistance Surrogates and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Among Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 Jun 7;16:1685-1696. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S409983. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 37309507 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Insulin Resistance in NAFLD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Focused on HOMA-IR in South Asians.Cureus. 2024 Oct 3;16(10):e70768. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70768. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39364176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triglyceride glucose waist circumference and non alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 May 1;25(1):328. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03888-x. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40312323 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Non-linear association between metabolic score for insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: analysis of US National health and nutrition examination survey data, 2017-2020.BMC Endocr Disord. 2025 Jul 14;25(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12902-025-01988-z. BMC Endocr Disord. 2025. PMID: 40660147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology. 2012;55(6):2005–2023. doi:10.1002/hep.25762 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

