Escherichia coli O157:H7 tir 255 T > A allele strains differ in chromosomal and plasmid composition
- PMID: 38169669
- PMCID: PMC10758439
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1303387
Escherichia coli O157:H7 tir 255 T > A allele strains differ in chromosomal and plasmid composition
Abstract
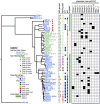
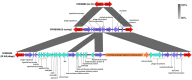
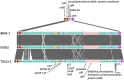
Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) O157:H7 strains with the T allele in the translocated intimin receptor polymorphism (tir) 255 A > T gene associate with human disease more than strains with an A allele; however, the allele is not thought to be the direct cause of this difference. We sequenced a diverse set of STEC O157:H7 strains (26% A allele, 74% T allele) to identify linked differences that might underlie disease association. The average chromosome and pO157 plasmid size and gene content were significantly greater within the tir 255 A allele strains. Eighteen coding sequences were unique to tir 255 A allele chromosomes, and three were unique to tir 255 T allele chromosomes. There also were non-pO157 plasmids that were unique to each tir 255 allele variant. The overall average number of prophages did not differ between tir 255 allele strains; however, there were different types between the strains. Genomic and mobile element variation linked to the tir 255 polymorphism may account for the increased frequency of the T allele isolates in human disease.
Keywords: Bacteriophage; Plasmids; STEC; Translocated Intimin Receptor; bacterial genomics; comparative genomics; whole genome sequencing (WGS).
Copyright © 2023 Weinroth, Clawson, Harhay, Eppinger, Harhay, Smith and Bono.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of Escherichia coli O157:H7 tir polymorphisms with human infection.BMC Infect Dis. 2007 Aug 24;7:98. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-7-98. BMC Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17718910 Free PMC article.
-
Rates of evolutionary change of resident Escherichia coli O157:H7 differ within the same ecological niche.BMC Genomics. 2022 Apr 7;23(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08497-6. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35392797 Free PMC article.
-
Translocated intimin receptors (Tir) of Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli isolates belonging to serogroups O26, O111, and O157 react with sera from patients with hemolytic-uremic syndrome and exhibit marked sequence heterogeneity.Infect Immun. 1998 Nov;66(11):5580-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.11.5580-5586.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9784578 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence and genetic characterization of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli on bovine and pork carcasses and the environment from transport trucks.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Apr 28;39(7):174. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03624-1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37115263
-
Comparative genomics analysis and characterization of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 strains reveal virulence genes, resistance genes, prophages and plasmids.BMC Genomics. 2023 Dec 20;24(1):791. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09902-4. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 38124028 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pathogenomes of Shiga Toxin Positive and Negative Escherichia coli O157:H7 Strains TT12A and TT12B: Comprehensive Phylogenomic Analysis Using Closed Genomes.Microorganisms. 2024 Mar 29;12(4):699. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12040699. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38674643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asadulghani M., Ogura Y., Ooka T., Itoh T., Sawaguchi A., Iguchi A., et al. . (2009). The defective prophage pool of Escherichia coli O157: prophage–prophage interactions potentiate horizontal transfer of virulence determinants. PLoS Pathog. 5:e1000408. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000408, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Besser T. E., Shaikh N., Holt N. J., Tarr P. I., Konkel M. E., Malik-Kale P., et al. . (2007). Greater diversity of Shiga toxin-encoding bacteriophage insertion sites among Escherichia coli O157:H7 isolates from cattle than in those from humans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74:554. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02632-07 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bielaszewska M., Prager R., Zhang W., Friedrich A. W., Mellmann A., Tschäpe H., et al. . (2006). Chromosomal dynamism in progeny of outbreak-related sorbitol-fermenting enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:NM. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 1900–1909. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.3.1900-1909.2006, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

