Advances in the role of microRNAs associated with the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in lung cancer
- PMID: 38169723
- PMCID: PMC10758458
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1279822
Advances in the role of microRNAs associated with the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in lung cancer
Abstract
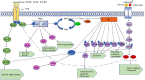
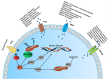
Cancer has long been a topic of great interest in society and a major factor affecting human health. Breast, prostate, lung, and colorectal cancers are the top four tumor types with the greatest incidence rates in 2020, according to the most recent data on global cancer incidence. Among these, lung cancer had the highest fatality rate. Extensive research has shown that microRNAs, through different signaling pathways, play crucial roles in cancer development. It is considered that the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway plays a significant role in the development of lung cancer. MicroRNAs can act as a tumor suppressor or an oncogene by altering the expression of important proteins in this pathway, such as PTEN and AKT. In order to improve the clinical translational benefit of microRNAs in lung cancer research, we have generalized and summarized the way of action of microRNAs linked with the PI3/AKT signaling pathway in this review through literature search and data analysis.
Keywords: MDR; PI3K/AKT; lung cancer; microRNA; therapy.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Zhang and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of microRNAs involved in PI3-kinase signaling pathway in colorectal cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2019 May;234(5):5664-5673. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27415. Epub 2018 Nov 29. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30488557 Review.
-
Roles of the RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathways in malignant transformation and drug resistance.Adv Enzyme Regul. 2006;46:249-79. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2006.01.004. Epub 2006 Jul 18. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2006. PMID: 16854453
-
Small in Size, but Large in Action: microRNAs as Potential Modulators of PTEN in Breast and Lung Cancers.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 18;11(2):304. doi: 10.3390/biom11020304. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33670518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-92a promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer metastasis.Int J Oncol. 2017 Jul;51(1):235-244. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.3999. Epub 2017 May 16. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28534966
-
A literature review of microRNA and gene signaling pathways involved in the apoptosis pathway of lung cancer.Respir Res. 2023 Feb 17;24(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02366-w. Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 36800962 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Decoding PTEN: from biological functions to signaling pathways in tumors.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Oct 24;51(1):1089. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10049-y. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39446204 Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs and regulation of the PI3K signaling pathway in lung cancer: Recent insights and potential clinical applications.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Dec 3;11:1-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.11.006. eCollection 2025 Apr. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 39720352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sishen Pill and its active phytochemicals in treating inflammatory bowel disease and colon cancer: an overview.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 8;15:1375585. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1375585. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38650627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNA Vav3 mediated ALV-J inhibition of autophagy by modulating the gga-miR-375/CIP2A axis and activating AKT.Poult Sci. 2025 Apr;104(4):104923. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.104923. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39987600 Free PMC article.
-
GART promotes the proliferation and migration of human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines A549 and H1299 by targeting PAICS-Akt-β-catenin pathway.Front Oncol. 2025 Mar 25;15:1543463. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1543463. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40201340 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

