A novel ERβ high throughput microscopy platform for testing endocrine disrupting chemicals
- PMID: 38169792
- PMCID: PMC10758781
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23119
A novel ERβ high throughput microscopy platform for testing endocrine disrupting chemicals
Abstract
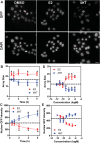
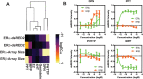
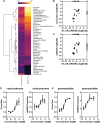
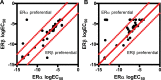
In this study we present an inducible biosensor model for the Estrogen Receptor Beta (ERβ), GFP-ERβ:PRL-HeLa, a single-cell-based high throughput (HT) in vitro assay that allows direct visualization and measurement of GFP-tagged ERβ binding to ER-specific DNA response elements (EREs), ERβ-induced chromatin remodeling, and monitor transcriptional alterations via mRNA fluorescence in situ hybridization for a prolactin (PRL)-dsRED2 reporter gene. The model was used to accurately (Z' = 0.58-0.8) differentiate ERβ-selective ligands from ERα ligands when treated with a panel of selective agonists and antagonists. Next, we tested an Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)-provided set of 45 estrogenic reference chemicals with known ERα in vivo activity and identified several that activated ERβ as well, with varying sensitivity, including a subset that is completely novel. We then used an orthogonal ERE-containing transgenic zebrafish (ZF) model to cross validate ERβ and ERα selective activities at the organism level. Using this environmentally relevant ZF assay, some compounds were confirmed to have ERβ activity, validating the GFP-ERβ:PRL-HeLa assay as a screening tool for potential ERβ active endocrine disruptors (EDCs). These data demonstrate the value of sensitive multiplex mechanistic data gathered by the GFP-ERβ:PRL-HeLa assay coupled with an orthogonal zebrafish model to rapidly identify environmentally relevant ERβ EDCs and improve upon currently available screening tools for this understudied nuclear receptor.
Keywords: Endocrine disruptors; Estrogen receptor alpha; Estrogen receptor beta; High content analysis; High throughput microscopy; Zebrafish.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Jia M., Dahlman-Wright K., Gustafsson J.Å. Estrogen receptor alpha and beta in health and disease. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;29(4):557–568. - PubMed
-
- Barros R.P.A., Gustafsson J.Å. Estrogen receptors and the metabolic network. Cell Metab. 2011;14(3):289–299. - PubMed
-
- Minutolo F., Macchia M., Katzenellenbogen B.S., Katzenellenbogen J.A. Estrogen receptor β ligands: recent advances and biomedical applications. Med. Res. Rev. 2011;31(3):364–442. - PubMed
-
- Katzenellenbogen B.S., Choi I., Delage-Mourroux R., Ediger T.R., Martini P.G., Montano M., et al. Molecular mechanisms of estrogen action: selective ligands and receptor pharmacology. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000;74(5):279–285. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

