Computed tomographic characterization of urinary stones in patients with urolithiasis from Southeast Mexico
- PMID: 38169908
- PMCID: PMC10758874
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23547
Computed tomographic characterization of urinary stones in patients with urolithiasis from Southeast Mexico
Abstract
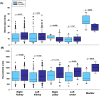
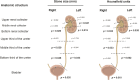
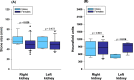
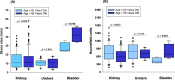
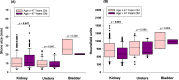
Urolithiasis (UL) is a severe public health concern in southeastern Mexico. Computed tomography (CT) is the first-line diagnostic method for patients with suspected UL. The present study aimed to characterize stones in the entire urinary system using CT and to contribute to personalized treatment in patients with UL. Patients >18 years of age with suspected UL were enrolled. Characteristics of UL included stone size, location (kidney, ureters, and bladder), composition of the stone in Hounsfield units (HU), presence of staghorn stone(s), and obstructive uropathy. Patients were stratified according to sex and age to determine whether stone size and HU were dependent on hormonal factors in females and on prostatic hyperplasia in males. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare median values. Frequencies are expressed as percentages and were analyzed using the Mantel-Haenszel chi-squared test. A total of 1150 patients were included in this study, of whom 744 (64.7 %) had UL in only 1 anatomical location in the urinary system, and 406 (35.3 %) had stones in ≥2 anatomical locations. Localization and stone size differed between males and females (p < 0.05). Additionally, males exhibited differences in HU (p = 0.024) and frequency of obstructive uropathy (p = 0.10) when stratified according to age (≤50 and > 50 years). In addition, females exhibited statistical differences in HU (p = 0.010) and kidney stone size (p = 0.047) dependent on age (≤47 and > 47 years). In conclusion, findings suggest that HU and stone size differ in different anatomical structures of the urinary system. In addition, differences in stone size and composition may be associated with age and sex.
Keywords: CT scan; Hounsfield units; Mexican population; Stone size.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The comparative survey of Hounsfield units of stone composition in urolithiasis patients.J Res Med Sci. 2014 Jul;19(7):650-3. J Res Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 25364366 Free PMC article.
-
Hounsfield unit density in the determination of urinary stone composition.Urology. 2001 Aug;58(2):170-3. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(01)01115-3. Urology. 2001. PMID: 11489691
-
Impact of urinary stone volume on computed tomography stone attenuations measured in Hounsfield units in a large group of Austrian patients with urolithiasis.Cent European J Urol. 2014;67(3):289-95. doi: 10.5173/ceju.2014.03.art16. Epub 2014 Aug 18. Cent European J Urol. 2014. PMID: 25247090 Free PMC article.
-
Radiopacity and hounsfield attenuation of cystine urolithiasis: case series and review of the literature.J Endourol. 2014 Apr;28(4):472-5. doi: 10.1089/end.2013.0524. Epub 2013 Dec 30. J Endourol. 2014. PMID: 24228639 Review.
-
Usefulness of hounsfield unit and density in the assessment and treatment of urinary stones.World J Nephrol. 2014 Nov 6;3(4):282-6. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v3.i4.282. World J Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 25374823 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Parotid sialolithiasis - Long term follow-up analyzing surgical approaches.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2024 Nov 7;9(6):e70030. doi: 10.1002/lio2.70030. eCollection 2024 Dec. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 39525521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen Z., Prosperi M., Bird V.Y. Prevalence of kidney stones in the USA: the national health and nutrition evaluation survey. J. Clin. Urol. 2019;12:296–302. doi: 10.1177/2051415818813820. - DOI
-
- Osther P.J. Springer; 2012. Epidemiology of Kidney Stones in the European Union.
-
- Gomez Orta F., Reyes Sosa G.R., Espinosa Said L., Arellano Perez H., Ortega M., Gomez Rodriguez R. [Algunos aspectos epidemiologicos de la litiasis renal en Mexico] Cir. Cir. 1984;1:365–375.
-
- Medina-Escobedo M., Zaidi M., Real-de León E., Orozco-Rivadeneyra S. Urolithiasis prevalence and risk factors in Yucatan, Mexico. Salud Publica Mex. 2002;44:541–545. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

