Effect of quercetin-loaded poly (lactic-co-glycolic) acid nanoparticles on lipopolysaccharide-induced memory decline, oxidative stress, amyloidogenesis, neurotransmission, and Nrf2/HO-1 expression
- PMID: 38169932
- PMCID: PMC10758873
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23527
Effect of quercetin-loaded poly (lactic-co-glycolic) acid nanoparticles on lipopolysaccharide-induced memory decline, oxidative stress, amyloidogenesis, neurotransmission, and Nrf2/HO-1 expression
Abstract
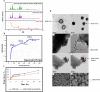
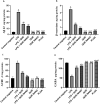
Neuroinflammation contributes to the pathogenesis of several neurodegenerative disorders. This study examined the neuroprotective effect of quercetin (QUR)-loaded poly (lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) nanoparticles (QUR NANO) against the neurotoxicity induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in mice. A QUR NANO formulation was prepared and characterized by differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray diffraction, entrapment efficiency (EE), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, field emission scanning electron microscopy, and in vitro drug release profile. Levels of glutathione, malondialdehyde, catalase, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), amyloid beta 42 (Aβ42), β-secretase, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and acetylcholine esterase (AChE) were measured in the mouse brain tissues. The gene expression of nuclear factor erythroid-related factor 2 (Nrf-2) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) were also determined. The prepared QUR NANO formulation showed 92.07 ± 3.21% EE and drug loading of 4.62 ± 0.55. It exhibited clusters of nano-spherical particles with smooth surface areas, and the loading process was confirmed. In vivo, the QUR NANO preserved the spatial memory of mice and protected the hippocampus from LPS-induced histological lesions. The QUR NANO significantly reduced the levels of malondialdehyde, iNOS, Aβ42, β-secretase, and AChE in brain tissue homogenates. Conversely, QUR NANO increased the glutathione, catalase, and GABA concentrations and upregulated the expression of Nrf-2 and HO-1 genes. Remarkably, the neuroprotective effect of QUR NANO was significantly greater than that of herbal QUR. In summary, the prepared QUR NANO formulation was efficient in mitigating LPS-induced neurotoxicity by reducing memory loss, oxidative stress, and amyloidogenesis while preserving neurotransmission and upregulating the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 genes. This study addresses several key factors in neuroinflammatory disorders and explores the potential of QUR-loaded nanoparticles as a novel therapeutic approach to alleviate these factors.
Keywords: Amyloid beta; Antioxidant; Brain; Nanoparticles; Quercetin.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

