Activation of endogenous glucocorticoids by HSD11B1 inhibits the antitumor immune response in renal cancer
- PMID: 38170044
- PMCID: PMC10761155
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2023.2286820
Activation of endogenous glucocorticoids by HSD11B1 inhibits the antitumor immune response in renal cancer
Abstract
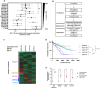
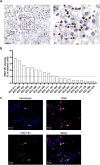
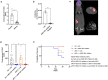
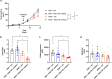
Although immune-based therapies have revolutionized the management of cancer, novel approaches are urgently needed to improve their outcome. We investigated the role of endogenous steroids in the resistance to cancer immunotherapy, as these have strong immunomodulatory functions. Using a publicly available database, we found that the intratumoral expression of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (HSD11B1), which regenerates inactive glucocorticoids into active glucocorticoids, was associated with poor clinical outcome and correlated with immunosuppressive gene signatures in patients with renal cell carcinoma (RCC). HSD11B1 was mainly expressed in tumor-infiltrating immune myeloid cells as seen by immunohistochemistry in RCC patient samples. Using peripheral blood mononuclear cells from healthy donors or immune cells isolated from the tumor of RCC patients, we showed that the pharmacological inhibition of HSD11B1 improved the response to the immune checkpoint inhibitor anti-PD-1. In a subcutaneous mouse model of renal cancer, the combination of an HSD11B1 inhibitor with anti-PD-1 treatment increased the proportion of tumor-infiltrating dendritic cells. In an intrarenal mouse tumor model, HSD11B1 inhibition increased the survival of mice treated with anti-PD-1. In addition, inhibition of HSD11B1 sensitized renal tumors in mice to immunotherapy with resiquimod, a Toll-like receptor 7 agonist. Mechanistically, we demonstrated that HSD11B1 inhibition combined with resiquimod increased T cell-mediated cytotoxicity to tumor cells by stimulating the antigen-presenting capacity of dendritic cells. In conclusion, these results support the use of HSD11B1 inhibitors to improve the outcome of immunotherapy in renal cancer and highlight the role of the endogenous glucocorticoid metabolism in the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Keywords: Glucocorticoids; HSD11B1; immunotherapy; renal cancer; steroidogenesis.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published with license by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures


References
-
- Albiges L, Tannir NM, Burotto M, McDermott D, Plimack ER, Barthélémy P, Porta C, Powles T, Donskov F, George S, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib for first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended 4-year follow-up of the phase III CheckMate 214 trial. ESMO Open. 2020;5(6):e001079. doi:10.1136/esmoopen-2020-001079. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Horvat TZ, Adel NG, Dang TO, Momtaz P, Postow MA, Callahan MK, Carvajal RD, Dickson MA, D’Angelo SP, Woo KM, et al. Immune-related adverse events, need for systemic immunosuppression, and effects on survival and time to treatment failure in patients with melanoma treated with ipilimumab at memorial sloan Kettering cancer center. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(28):3193–3198. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.60.8448. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
