HKDC1, a target of TFEB, is essential to maintain both mitochondrial and lysosomal homeostasis, preventing cellular senescence
- PMID: 38170752
- PMCID: PMC10786298
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2306454120
HKDC1, a target of TFEB, is essential to maintain both mitochondrial and lysosomal homeostasis, preventing cellular senescence
Erratum in
-
Correction for Cui et al., HKDC1, a target of TFEB, is essential to maintain both mitochondrial and lysosomal homeostasis, preventing cellular senescence.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Oct 8;121(41):e2418618121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2418618121. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39348551 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
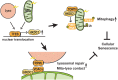
Mitochondrial and lysosomal functions are intimately linked and are critical for cellular homeostasis, as evidenced by the fact that cellular senescence, aging, and multiple prominent diseases are associated with concomitant dysfunction of both organelles. However, it is not well understood how the two important organelles are regulated. Transcription factor EB (TFEB) is the master regulator of lysosomal function and is also implicated in regulating mitochondrial function; however, the mechanism underlying the maintenance of both organelles remains to be fully elucidated. Here, by comprehensive transcriptome analysis and subsequent chromatin immunoprecipitation-qPCR, we identified hexokinase domain containing 1 (HKDC1), which is known to function in the glycolysis pathway as a direct TFEB target. Moreover, HKDC1 was upregulated in both mitochondrial and lysosomal stress in a TFEB-dependent manner, and its function was critical for the maintenance of both organelles under stress conditions. Mechanistically, the TFEB-HKDC1 axis was essential for PINK1 (PTEN-induced kinase 1)/Parkin-dependent mitophagy via its initial step, PINK1 stabilization. In addition, the functions of HKDC1 and voltage-dependent anion channels, with which HKDC1 interacts, were essential for the clearance of damaged lysosomes and maintaining mitochondria-lysosome contact. Interestingly, HKDC1 regulated mitophagy and lysosomal repair independently of its prospective function in glycolysis. Furthermore, loss function of HKDC1 accelerated DNA damage-induced cellular senescence with the accumulation of hyperfused mitochondria and damaged lysosomes. Our results show that HKDC1, a factor downstream of TFEB, maintains both mitochondrial and lysosomal homeostasis, which is critical to prevent cellular senescence.
Keywords: HKDC1; TFEB; cellular senescence; mitochondria–lysosome contact; mitophagy.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:T. Yoshimori and S.N. are founders of AutoPhagyGO.
Figures
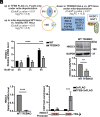
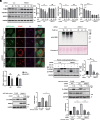
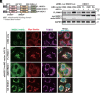


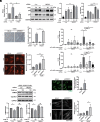
References
-
- Deus C. M., Yambire K. F., Oliveira P. J., Raimundo N., Mitochondria-lysosome crosstalk: From physiology to neurodegeneration. Trends Mol. Med. 26, 71–88 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 23K18140/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 22H04982/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- N/A/Astellas Foundation for Research on Metabolic Disorders
- N/A/Takeda Science Foundation (TSF)
- N/A/Mitsubishi Foundation (The Mitsubishi Foundation)
- 21H02428/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- S10 OD027016/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- N/A/Mochida Memorial Foundation for Medical and Pharmaceutical Research ( )
- T32 AG057468/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- JPMJCR17H6/MEXT | JST | Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology (CREST)
- JP22gm1410014/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
- 21H05145/Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT)
- N/A/NOVARTIS Foundation (Japan) for the Promotion of Science (NOVARTIS Foundation (Japan))
- N/A/China Scholarship Council (CSC)
- 23jm0610091h0001/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

