Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution over 100-km fiber with local local oscillator
- PMID: 38170766
- PMCID: PMC10776027
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adi9474
Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution over 100-km fiber with local local oscillator
Abstract
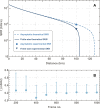
Quantum key distribution (QKD) enables two remote parties to share encryption keys with security based on the laws of physics. Continuous-variable (CV) QKD with coherent states and coherent detection integrates well with existing telecommunication networks. Thus far, long-distance CV-QKD has only been demonstrated using a highly complex scheme where the local oscillator is transmitted, opening security loopholes for eavesdroppers and limiting potential applications. Here, we report a long-distance CV-QKD experiment with a locally generated local oscillator over a 100-kilometer fiber channel with a total loss of 15.4 decibels. This record-breaking distance is achieved by controlling the phase noise-induced excess noise through a machine learning framework for carrier recovery and optimizing the modulation variance. We implement the full CV-QKD protocol and demonstrate the generation of keys secure against collective attacks in the finite-size regime. Our results mark a substantial milestone for realizing CV quantum access networks with a high loss budget and pave the way for large-scale deployment of secure QKD.
Figures


References
-
- Hellman M., New directions in cryptography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 22, 644–654 (1976).
-
- Rivest R. L., Shamir A., Adleman L., A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems. Commun. ACM 21, 120–126 (1978).
-
- P. W. Shor, Algorithms for quantum computation: Discrete logarithms and factoring, in Proceedings 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (IEEE, 1994), pp. 124–134.
-
- Arute F., Arya K., Babbush R., Bacon D., Bardin J. C., Barends R., Biswas R., Boixo S., Brandao F. G. S. L., Buell D. A., Burkett B., Chen Y., Chen Z., Chiaro B., Collins R., Courtney W., Dunsworth A., Farhi E., Foxen B., Fowler A., Gidney C., Giustina M., Graff R., Guerin K., Habegger S., Harrigan M. P., Hartmann M. J., Ho A., Hoffmann M., Huang T., Humble T. S., Isakov S. V., Jeffrey E., Jiang Z., Kafri D., Kechedzhi K., Kelly J., Klimov P. V., Knysh S., Korotkov A., Kostritsa F., Landhuis D., Lindmark M., Lucero E., Lyakh D., Mandrà S., McClean J. R., McEwen M., Megrant A., Mi X., Michielsen K., Mohseni M., Mutus J., Naaman O., Neeley M., Neill C., Niu M. Y., Ostby E., Petukhov A., Platt J. C., Quintana C., Rieffel E. G., Roushan P., Rubin N. C., Sank D., Satzinger K. J., Smelyanskiy V., Sung K. J., Trevithick M. D., Vainsencher A., Villalonga B., White T., Yao Z. J., Yeh P., Zalcman A., Neven H., Martinis J. M., Quantum supremacy using a programmable superconducting processor. Nature 574, 505–510 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Bennett C. H., Brassard G., Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing. Theor. Comp. Sci. 560, 7– 11547 (2014).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

