Deciphering microglia phenotypes in health and disease
- PMID: 38171044
- PMCID: PMC12118495
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gde.2023.102146
Deciphering microglia phenotypes in health and disease
Abstract
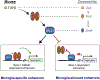
Microglia are the major immune cells of the central nervous system (CNS) that perform numerous adaptive functions required for normal CNS development and homeostasis but are also linked to neurodegenerative and behavioral diseases. Microglia development and function are strongly influenced by brain environmental signals that are integrated at the level of transcriptional enhancers to drive specific programs of gene expression. Here, we describe a conceptual framework for how lineage-determining and signal-dependent transcription factors interact to select and regulate the ensembles of enhancers that determine microglia development and function. We then highlight recent findings that advance these concepts and conclude with a consideration of open questions that represent some of the major hurdles to be addressed in the future.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kierdorf K, Erny D, Goldmann T, Sander V, Schulz C, Perdiguero EG, Wieghofer P, Heinrich A, Riemke P, Holscher C, et al.: Microglia emerge from erythromyeloid precursors via Pu.1- and Irf8-dependent pathways. Nat Neurosci 2013, 16:273–280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

