Inhibition of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 during Serum Deprivation Increases Hepatic Gluconeogenesis via the AMPK/AKT/FOXO Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 38171209
- PMCID: PMC10901661
- DOI: 10.3803/EnM.2023.1786
Inhibition of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 during Serum Deprivation Increases Hepatic Gluconeogenesis via the AMPK/AKT/FOXO Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Backgruound: Sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) mediates glucose reabsorption in the renal proximal tubules, and SGLT2 inhibitors are used as therapeutic agents for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. This study aimed to elucidate the effects and mechanisms of SGLT2 inhibition on hepatic glucose metabolism in both serum deprivation and serum supplementation states.
Methods: Huh7 cells were treated with the SGLT2 inhibitors empagliflozin and dapagliflozin to examine the effect of SGLT2 on hepatic glucose uptake. To examine the modulation of glucose metabolism by SGLT2 inhibition under serum deprivation and serum supplementation conditions, HepG2 cells were transfected with SGLT2 small interfering RNA (siRNA), cultured in serum-free Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium for 16 hours, and then cultured in media supplemented with or without 10% fetal bovine serum for 8 hours.
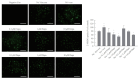
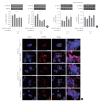
Results: SGLT2 inhibitors dose-dependently decreased hepatic glucose uptake. Serum deprivation increased the expression levels of the gluconeogenesis genes peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma co-activator 1 alpha (PGC-1α), glucose 6-phosphatase (G6pase), and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK), and their expression levels during serum deprivation were further increased in cells transfected with SGLT2 siRNA. SGLT2 inhibition by siRNA during serum deprivation induces nuclear localization of the transcription factor forkhead box class O 1 (FOXO1), decreases nuclear phosphorylated-AKT (p-AKT), and p-FOXO1 protein expression, and increases phosphorylated-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (p-AMPK) protein expression. However, treatment with the AMPK inhibitor, compound C, reversed the reduction in the protein expression levels of nuclear p- AKT and p-FOXO1 and decreased the protein expression levels of p-AMPK and PEPCK in cells transfected with SGLT2 siRNA during serum deprivation.
Conclusion: These data show that SGLT2 mediates glucose uptake in hepatocytes and that SGLT2 inhibition during serum deprivation increases gluconeogenesis via the AMPK/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway.
Keywords: AMP-activated protein kinases; FOXO1; Gluconeogenesis; Hepatocytes; Serum deprivation; Sodium-dependent glucose transporter 2.
Conflict of interest statement
Won-Young Lee is an editor-in-chief and Eun-Jung Rhee is a deputy editor of the journal. But they were not involved in the peer reviewer selection, evaluation, or decision process of this article. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures



References
-
- Kim JH, Ko HY, Wang HJ, Lee H, Yun M, Kang ES. Effect of dapagliflozin, a sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, on gluconeogenesis in proximal renal tubules. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020;22:373–82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

