Cardiac Blood-Based Biomarkers of Myocardial Stress as Predictors of Atrial Fibrillation Development in Patients With Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source/Cryptogenic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38171502
- PMCID: PMC11076184
- DOI: 10.3988/jcn.2023.0068
Cardiac Blood-Based Biomarkers of Myocardial Stress as Predictors of Atrial Fibrillation Development in Patients With Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source/Cryptogenic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background and purpose: Undiagnosed atrial fibrillation (AF) is a major risk factor for stroke that can go unnoticed in individuals with embolic stroke of undetermined source (ESUS) or cryptogenic stroke (CS). Early detection is critical for stroke prognosis and secondary prevention. This study aimed to determine if blood biomarkers of myocardial stress can accurately predict AF in patients with ESUS/CS, which would allow the identification of those who would benefit from closer monitoring.
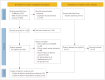
Methods: In February 2023 we performed a systematic date-unrestricted search of three databases for studies on patients with ESUS/CS who were subsequently diagnosed with AF. We examined the relationships between AF and serum myocardial stress markers such as brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), N-terminal-pro-BNP (NT-proBNP), midregional proatrial natriuretic peptide, and troponin.
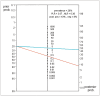
Results: Among the 1,527 studies reviewed, 23 eligible studies involving 6,212 participants, including 864 with AF, were analyzed. A meta-analysis of 9 studies indicated that they demonstrated a clear association between higher NT-proBNP levels and an increased risk of AF, with adjusted and raw data indicating 3.06- and 9.03-fold higher AF risks, respectively. Lower NT-proBNP levels had a pooled negative predictive value of 91.7%, indicating the potential to rule out AF with an 8% false-negative rate.
Conclusions: Further research is required to fully determine the potential of biomarkers for AF detection after stroke, as results from previous studies lack homogeneity. However, lower NT-proBNP levels have potential in ruling out AF in patients with ESUS/CS. Combining them with other relevant biomarkers may enhance the precision of identifying patients who will not benefit from extended monitoring, which would optimize resource allocation and patient care.
Keywords: BNP; ESUS; atrial fibrillation; biomarker; cryptogenic stroke.
Copyright © 2024 Korean Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
B-type natriuretic peptide over N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide to predict incident atrial fibrillation after cryptogenic stroke.Eur J Neurol. 2021 Feb;28(2):540-547. doi: 10.1111/ene.14579. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Eur J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33043545
-
Predictors of Atrial Fibrillation Development in Patients With Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source: An Analysis of the RE-SPECT ESUS Trial.Circulation. 2021 Nov 30;144(22):1738-1746. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.055176. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Circulation. 2021. PMID: 34649459 Clinical Trial.
-
Biomarkers predictive of atrial fibrillation in patients with cryptogenic stroke. Insights from the Nordic Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke (NOR-FIB) study.Eur J Neurol. 2023 May;30(5):1352-1363. doi: 10.1111/ene.15746. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Eur J Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36786305
-
Monitoring for atrial fibrillation prior to patent foramen ovale closure after cryptogenic stroke.Int J Stroke. 2023 Apr;18(4):400-407. doi: 10.1177/17474930221124412. Epub 2022 Sep 19. Int J Stroke. 2023. PMID: 36050817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atrial Fibrillation, thromboembolic risk, and the potential role of the natriuretic peptides, a focus on BNP and NT-proBNP - A narrative review.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2022 Oct 10;43:101132. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2022.101132. eCollection 2022 Dec. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2022. PMID: 36246770 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hart RG, Diener HC, Coutts SB, Easton JD, Granger CB, O’Donnell MJ, et al. Embolic strokes of undetermined source: the case for a new clinical construct. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13:429–438. - PubMed
-
- Saver JL. Cryptogenic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:2065–2074. - PubMed
-
- Sanna T, Diener HC, Passman RS, Di Lazzaro V, Bernstein RA, Morillo CA, et al. Cryptogenic stroke and underlying atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2478–2486. - PubMed
-
- Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist C, et al. 2020 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): the task force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2021;42:373–498. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

