Validation of Estimated Small Dense Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Concentration in a Japanese General Population
- PMID: 38171805
- PMCID: PMC11150720
- DOI: 10.5551/jat.64578
Validation of Estimated Small Dense Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Concentration in a Japanese General Population
Abstract
Aim: A high level of directly measured small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (sdLDL-C) is a strong risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. A method for estimating sdLDL-C by using Sampson's equation that includes levels of total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), non-HDL-C and triglycerides (TG) has recently been proposed. We investigated the validation and exploration of estimated sdLDL-C level.
Methods: The associations between measured and estimated sdLDL-C levels were investigated in 605 Japanese subjects (men/women: 280/325; mean age: 65±15 years) who received annual health check-ups in the Tanno-Sobetsu Study, a population-based cohort.
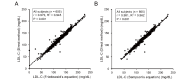
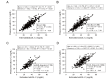
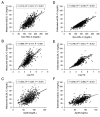
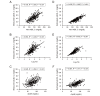
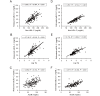
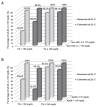
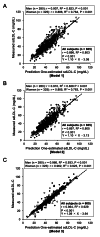
Results: Estimated sdLDL-C level was highly correlated with measured sdLDL-C level in all subjects (R2=0.701), nondiabetic subjects without any medication (n=254, R2=0.686) and subjects with diabetes mellitus (n=128, R2=0.721). Multivariable regression analysis showed that levels of non-HDL-C, TG and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (γGTP) were independent predictors of measured sdLDL-C level. In a stratification of the LDL window, all of the subjects with a combination of high non-HDL-C (≥ 170 mg/dL) and high TG (≥ 150 mg/dL) had high levels of measured and estimated sdLDL-C (≥ 35 mg/dL). Furthermore, machine learning-based estimation of sdLDL-C level by artificial intelligence software, Prediction One, was substantially improved by using components of Sampson's equation (R2=0.803) and by using those components with the addition of γGTP and deletion of TC (R2=0.929).
Conclusions: sdLDL-C level estimated by Sampson's equation can be used instead of measured sdLDL-C level in general practice. By building multiple machine learning models of artificial intelligence, a more accurate and practical estimation of sdLDL-C level might be possible.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Machine learning; Sampson’s equation; Small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; Validation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Austin MA, Breslow JL, Hennekens CH, Buring JE, Willett WC, Krauss RM: Low-density lipoprotein subclass patterns and risk of myocardial infarction. Jama, 1988; 260: 1917-1921 - PubMed
-
- Hirano T, Ito Y, Saegusa H, Yoshino G: A novel and simple method for quantification of small, dense LDL. J Lipid Res, 2003; 44: 2193-2201 - PubMed

