Systems-based identification of the Hippo pathway for promoting fibrotic mesenchymal differentiation in systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 38172207
- PMCID: PMC10764940
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-44645-6
Systems-based identification of the Hippo pathway for promoting fibrotic mesenchymal differentiation in systemic sclerosis
Abstract
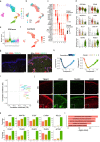
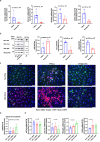
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a devastating autoimmune disease characterized by excessive production and accumulation of extracellular matrix, leading to fibrosis of skin and other internal organs. However, the main cellular participants in SSc skin fibrosis remain incompletely understood. Here using differentiation trajectories at a single cell level, we demonstrate a dual source of extracellular matrix deposition in SSc skin from both myofibroblasts and endothelial-to-mesenchymal-transitioning cells (EndoMT). We further define a central role of Hippo pathway effectors in differentiation and homeostasis of myofibroblast and EndoMT, respectively, and show that myofibroblasts and EndoMTs function as central communication hubs that drive key pro-fibrotic signaling pathways in SSc. Together, our data help characterize myofibroblast differentiation and EndoMT phenotypes in SSc skin, and hint that modulation of the Hippo pathway may contribute in reversing the pro-fibrotic phenotypes in myofibroblasts and EndoMTs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.E.G. has received Grant support from Celgene/BMS, Janssen, Eli Lilly, and Almirall. J.E.G. has served on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Janssen, Almirall, BMS. J.M.K. has received Grant support from Q32 Bio, Celgene/BMS, Ventus Therapeutics, and Janssen. J.M.K. has served on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Bristol Myers Squibb, Avion Pharmaceuticals, Provention Bio, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Ventus Therapeutics, Vera Therapeutics, and Boehringer Ingelheim. P.W.H. has received effort support from Q32 Bio. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AR073196/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR080612/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR077741/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007863/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM086262/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AR063120/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR040312/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AR076975/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR069071/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI144298/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR071384/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI022553/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR074302/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AR078251/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR075043/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR081640/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR072129/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

